Figure 1.
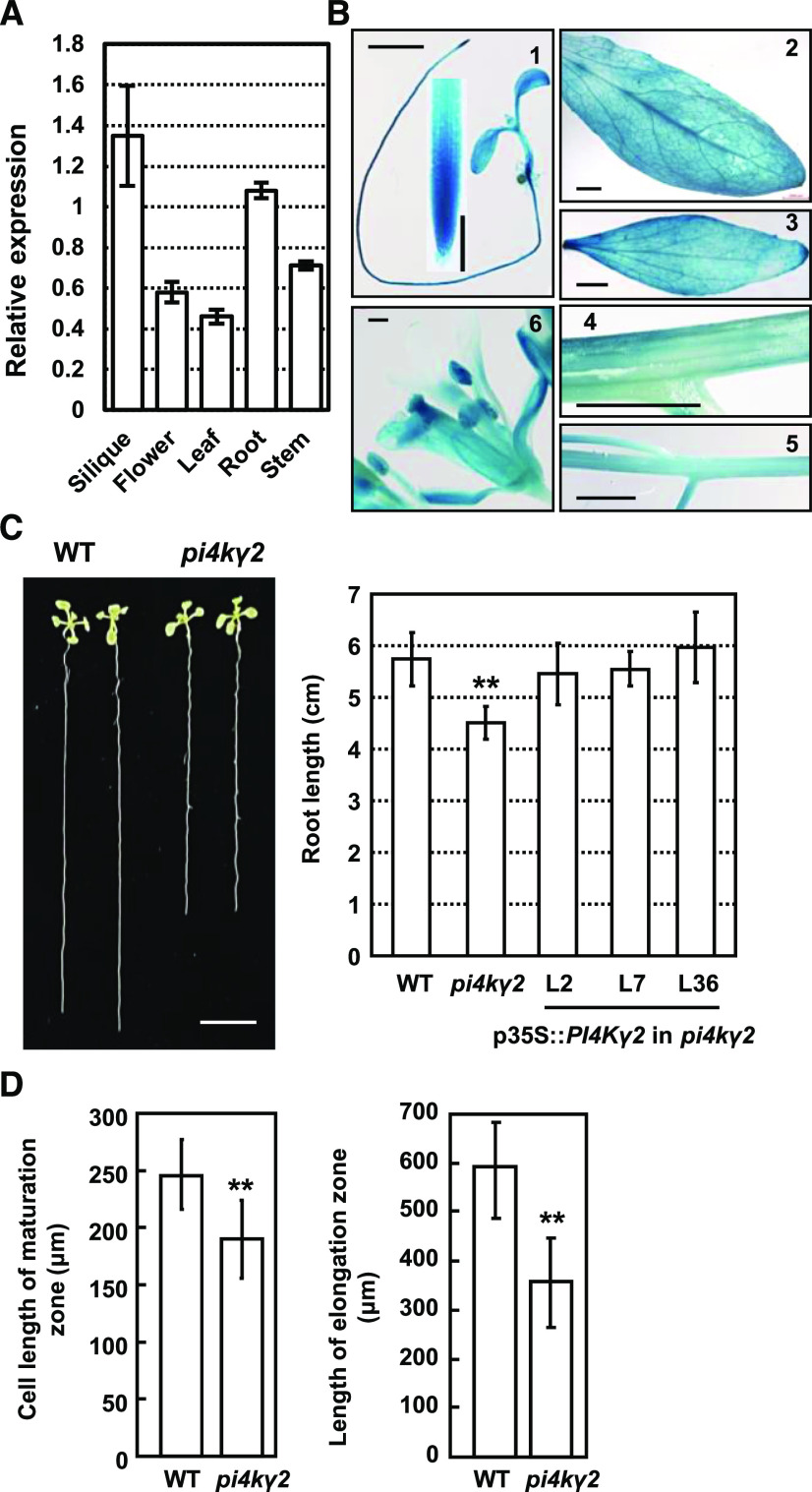
Deficiency of PI4Kγ2 results in shortened roots. A, RT-qPCR analysis revealed PI4Kγ2 expression in various tissues including leaf, stem, flower, root, and silique. ACTIN7 gene was used as an internal reference. Analysis were biologically repeated three times and data are presented as means ± se (n = 3). B, Promoter–GUS fusion analysis revealed that PI4Kγ2 is expressed in young seedlings (1), rosette leaf (2), cauline leaf (3), stem (4), inflorescence (5), and floral tissue (6). Scale bars = 200 μm (1 and 6) and 2 mm (2–5). C, Observation (left) and measurement (right) of root growth of 10-d–old wild-type (WT), pi4kγ2, and pi4kγ2 seedlings expressing p35S::PI4Kγ2-mCherry. Scale bar = 1 cm. Experiments were repeated three times and data are presented as means ± sd (n > 30). Statistical analysis revealed significant difference (**P < 0.01). D, pi4kγ2 plants exhibited a decreased root elongation zone length and root epidermal cell length in the maturation zone compared to those of wild type. Roots of 7-d–old seedlings were measured and statistically analyzed (**P < 0.01). Experiments were repeated three times and data are presented as means ± sd (n = 30).