Figure 5.
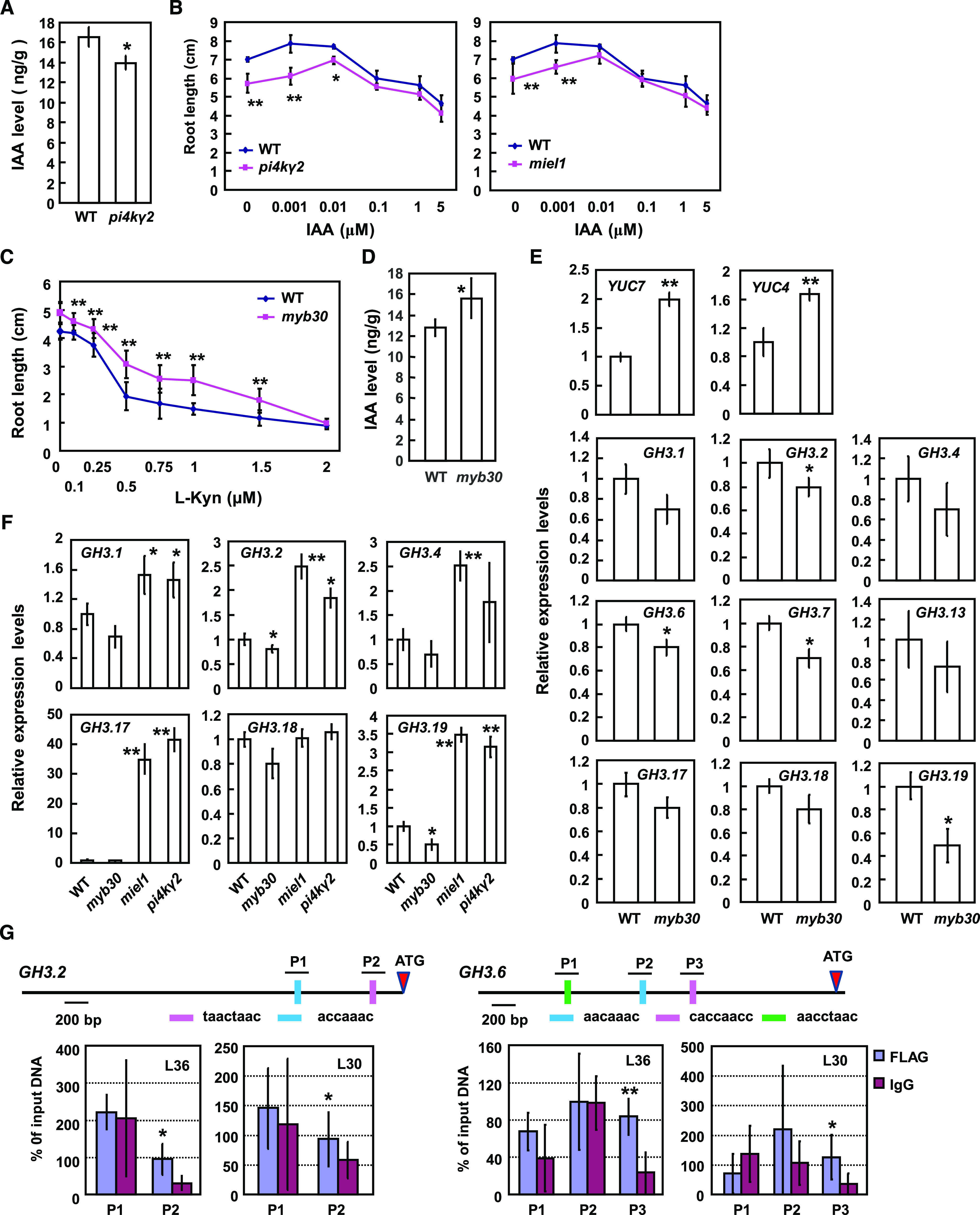
PI4Kγ2 deficiency results in reduced auxin level and MYB30 deficiency results in altered expression levels of GH3 or YUC genes in planta. A, Quantification of free IAA content by LC-MS revealed a reduced IAA level in pi4kγ2. Roots of 5-d-old wild-type (WT) and pi4kγ2 seedlings were used for analysis and data are presented as means ± sd (n = 5). Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed Student’s t test (*P < 0.05, compared to wild type). B, Wild-type, miel1, and pi4kγ2 seedlings were grown on Murashige-and-Skoog medium supplemented with IAA for 15 d, and root lengths were measured. Experiments were repeated three times and data are presented as means ± sd (n > 30). Statistical analysis revealed significant differences compared to wild type (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01). C, Wild-type and myb30 seedlings were grown on Murashige-and-Skoog medium supplemented with IAA biosynthesis inhibitor l-Kynurenine (l-Kyn) for 10 d, and root lengths were measured. Experiments were repeated three times and data are presented as means ± sd (n > 30). Statistical analysis revealed the significant differences compared to wild type (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01). D, Quantification of free IAA content by LC-MS revealed the increased IAA level in myb30. Roots of 5-d-old wild type and myb30 seedlings were used for analysis and data are presented as means ± sd (n = 5). Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed Student’s t test compared to wild type (*P < 0.05). E, Relative expression levels of YUCCA and GH3 genes in myb30 and wild type (expression of examined genes in wild type was set as “1”). Roots of 7-d–old seedlings were used for RNA extraction and RT-qPCR analysis. ACTIN7 gene was used as an internal reference. Experiments were repeated three times and data are presented as means ± se (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed Student’s t test compared to wild type (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01). F, Relative expression levels of GH3 genes in wild type, pi4kγ2, miel1, and myb30 (expression of examined genes in wild type was set as “1”). Roots of 7-d-old seedlings were used for RNA extraction and RT-qPCR analysis. ACTIN7 gene was used as an internal reference. Experiments were repeated three times and data are presented as means ± se (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed Student’s t test compared to wild type (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01). G, ChIP-qPCR analysis showed that MYB30 directly binds the promoter regions of GH3.2 and GH3.6 to regulate their expression. Two independent lines expressing MYB30-FLAG (L30 and L36) were used for analysis. Input DNA (from the un-immunoprecipitated DNA) was used as a positive control (100%). Immunoprecipitated DNA from IgG chromatin was used as a negative control. P1, P2, and P3 are the putative MYB30 binding sequences in promoters of GH3.2 and GH3.6. Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed Student’s t test compared to Input DNA (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01).
