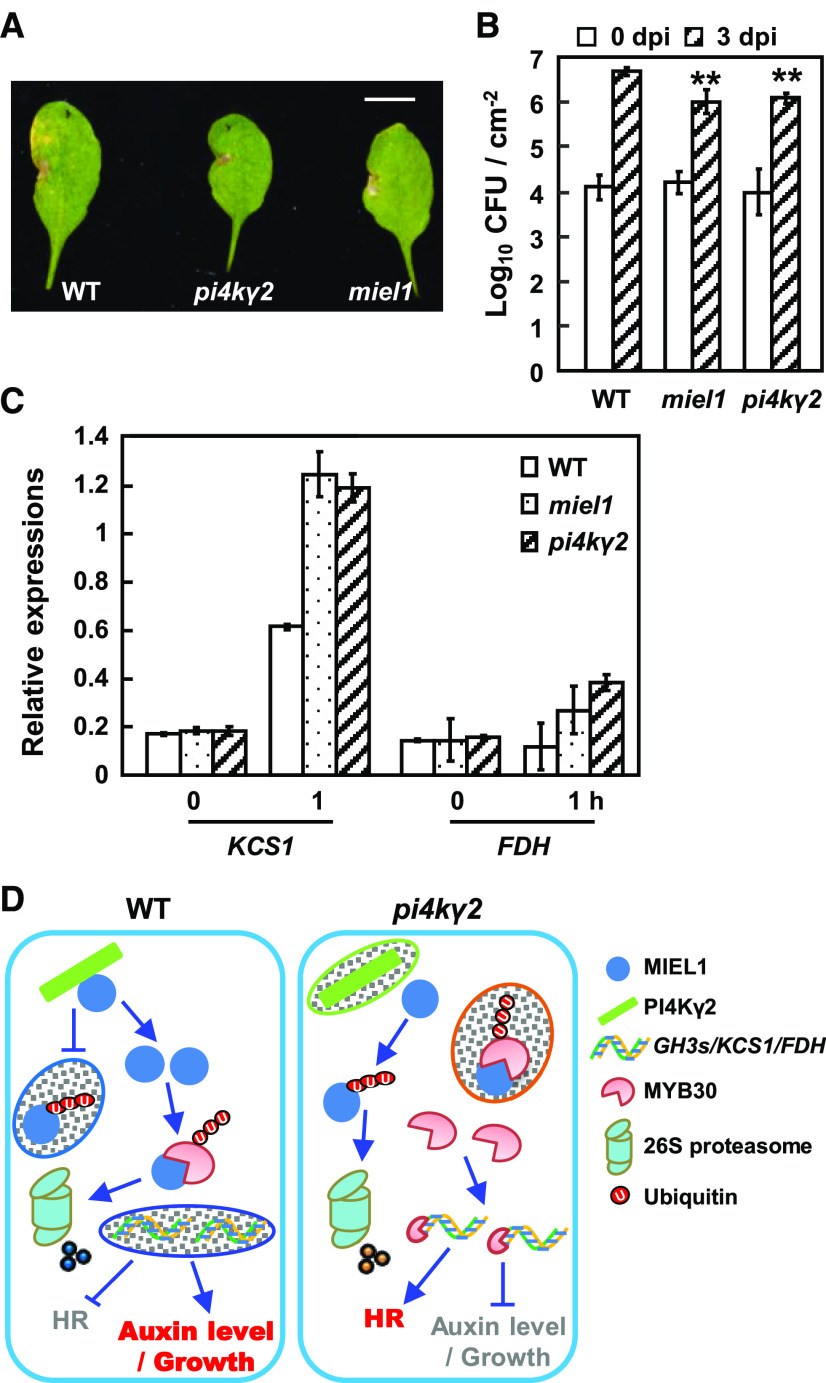
Figure 6.
PI4Kγ2 is a negative regulator of HR responses in response to bacterial inoculation. A, Symptoms developed by pi4kγ2, miel1, and wild-type (WT) 64 hpi with Pst AvrRpm1 (2 × 106 cfu mL−1). Experiments were repeated three times (>5 seedlings each time) and representative images were shown. Scale bar = 1 cm. B, Growth of Pst AvrRpm1 in pi4kγ2, miel1, and wild type. Bacterial growth at 3 d was measured after inoculation (5 × 105 cfu mL−1). Experiments were repeated three times and data are presented as means ± sd (n > 5). Statistical analysis revealed significant differences compared to wild type (**P < 0.01). C, Relative expression levels of KCS1 and FDH, the target genes for MYB30. Wild-type, pi4kγ2, and miel1 seedlings were used for extracting RNA after inoculation with Pst AvrRpm1 (5 × 107 cfu mL−1) for 1 h. ACTIN7 gene was used as an internal reference. Experiments were repeated three times and data are presented as means ± se (n = 3). D, Model illustrating the regulation of PI4Kγ2-MIEL1-MYB30 and the effects on plant growth and HR. In wild type, PI4Kγ2 interacts with MIEL1 to suppress its ubiquitination and degradation, leading to the proteasomal degradation of MYB30 by MIEL1. Reduced MYB30 protein results in increased auxin content/signaling, and in turn promoted growth and suppressed HR to avoid superfluous activation. Under PI4Kγ2 deficiency, enhanced MIEL1 ubiquitination and degradation results in the suppressed ubiquitination and degradation of MYB30. Accumulated MYB30 thereby activates the expression of target genes, resulting in decreased auxin level, suppressed growth, and stimulated HR.