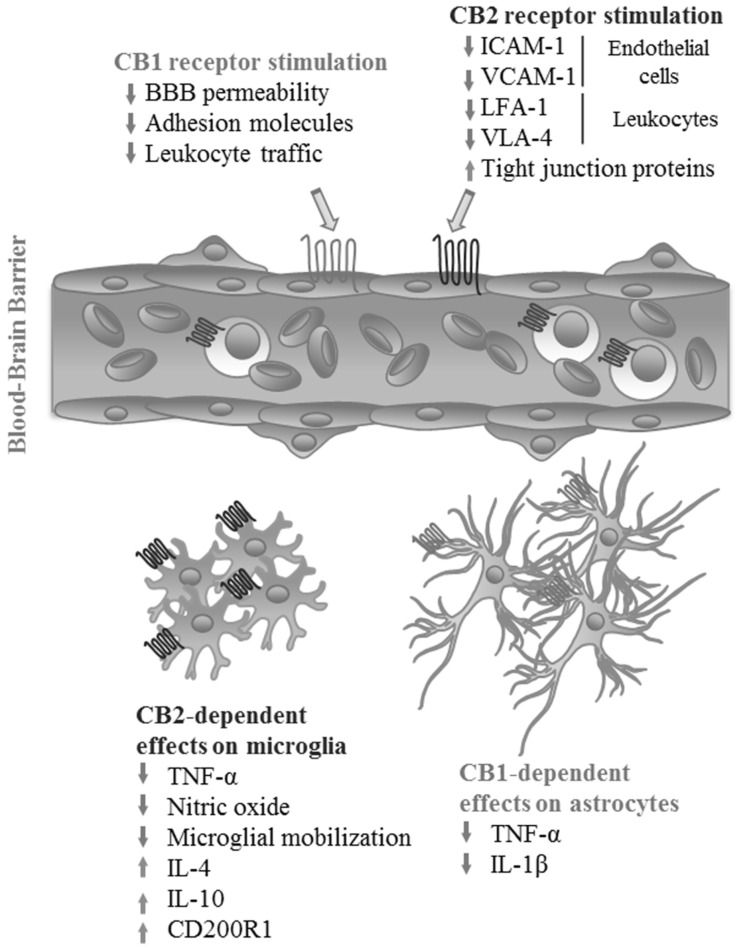
Fig. (1).
Effects of eCB receptor activation on the blood-brain barrier and glial inflammatory response. Activation of CB1 and CB2 receptors by their endogenous ligands or exogenous agonists at the BBB decreases endothelial permeability and leukocyte infiltration into the CNS by reducing the expression of intercellular adhesion molecules both at the endothelial layer and on leukocytes, while also increasing the expression of tight junction proteins. On glial cells, signaling through CB2 decreases production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide by microglia, while increasing the production of inhibitory molecules. In astrocytes, a similar effect is achieved by activation of CB1. (Figure created by the authors). (A higher resolution / colour version of this figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).