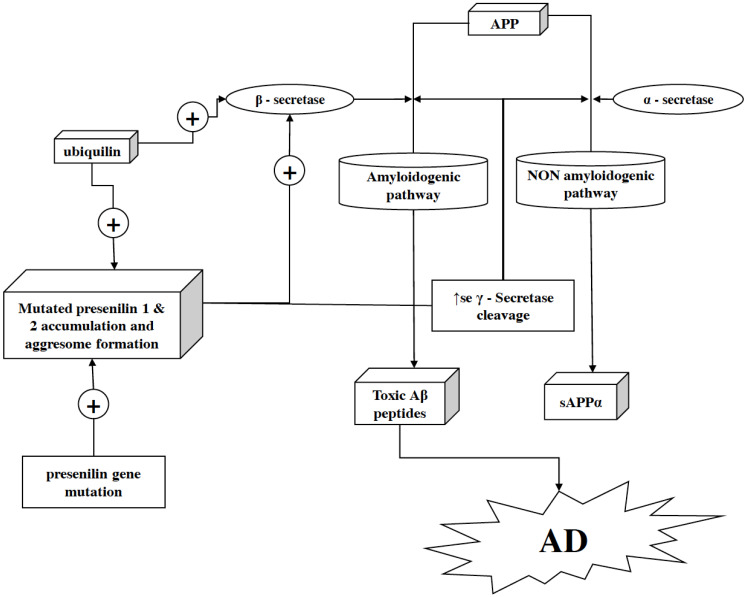
Fig. (3).
Role of presenilin in neurodegeneration. Presenilin proteins, i.e., presenilin 1 and presenilin 2 (along with other proteins), are structural units of γ-secretase complex. In the γ-secretase protein complex, presenilin acts as an active site after being cleaved into an N- and C-terminal fragment. Moreover, it helps the γ-secretase complex to exert its activity by letting the substrate pass through the hydrophilic pocket in the membrane formed by two presenilin fragments. Within the hydrophobic environment of the plasma membrane, γ-secretase cleaves the C-terminal fragment of APP after it gets cleaved by α- or β-secretase (in non-amyloidogenic and amyloidogenic pathways, respectively) to release the APP’s cytoplasmic domain. As a key factor in γ-secretase activity, the mutation in presenilin can facilitate overactivation of the amyloidogenic pathway and as a result, the production of Aβ–42 gets enhanced in the brain. In addition, ubiquilin-1 fuels this pathology more aggressively as it facilitates the presenilin 1 accumulation and aggresome formation by ubiquilin-1 transcript variant 1 and ubiquilin-1 transcript variant 2. (A higher resolution / colour version of this figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).