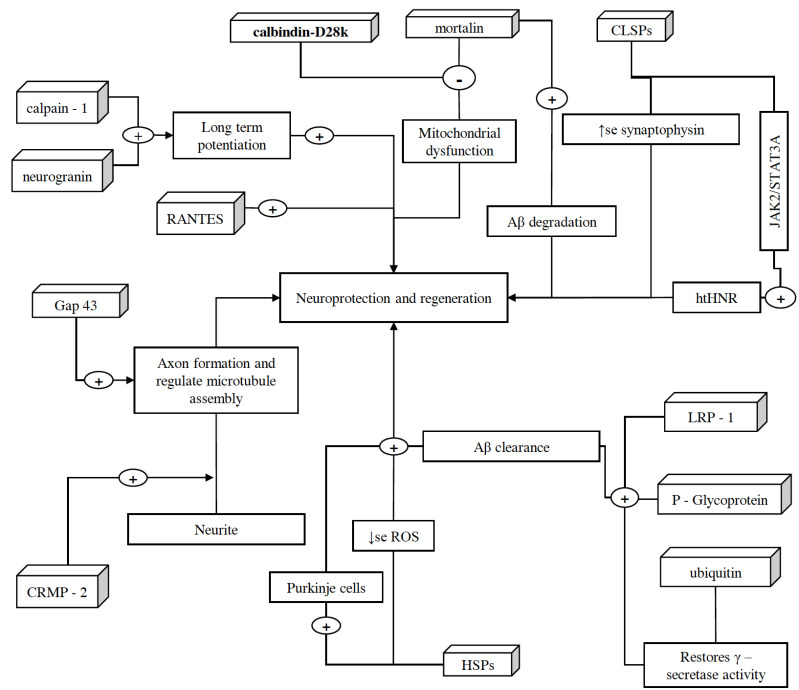
Fig. (4).
Schematic representation of proteins associated with neuroprotection and regeneration. These proteins help in the growth, regulation, and protection of neurons. CRMP-2, after getting phosphorylated by Rho-kinase and glycogen synthase, assists axon development, and binds/regulate microtubules assembly, respectively. Along with CRMP-2, GAP-43 also contributes to the growth of axons and modulates the formation of new connections. However, because of high lipid content and oxygen consumption in the brain, there is an increased amount of oxidative stress. In order to counteract this situation, brain expresses HSPs in different regions of CNS such as cortical region (especially in astrocytes). These HSPs also ameliorate the decline in Purkinje cells of the brain and halt neurodegeneration. CLSP exhibits neuroprotection by interacting with htHNR and inhibiting the loss of synaptophysin, which indeed facilitate detoxification and synaptic transmission via playing a crucial role in the biogenesis of secretory vesicles and prompting the targeting of VMATs towards these vesicles. In addition, calpain-1 also plays an important role in the initiation of LTP. On the other hand, ubiquitin helps in restoring the γ-secretase activity, clearing denatured protein fragments and insoluble aggregates such as Aβ plaques and NFTs via ubiquitin-dependent protein degradation system. P-glycoprotein and LRP-1, along with SORLA, also assist Aβ clearance and facilitate its transportation across the BBB. However, Aβ mediated microglia activation and therefore the expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, and NF-κB cause reduction in the expression of P-glycoprotein, which later is halted by Mortalin overexpression, as it extenuates Aβ mediated cell damage and apoptosis via inhibiting the mPTP, caspase-3 activation, and release of pro-apoptotic factor cytochrome C. Moreover, overexpressed mortalin, along with calbindin-D28k, regulates intracellular calcium concentrations, which help in reducing the oxidative stress and glutamate neurotoxicity. Moreover, increased RANTES expression is associated with the activation of PI-3K and MAPK signaling pathways and this phenomenon exhibits neuroprotection. However, the role of neurogranin in neuroprotection is yet to be discovered, it is believed to be facilitating the hippocampal synaptic plasticity and spatial learning. (A higher resolution / colour version of this figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).