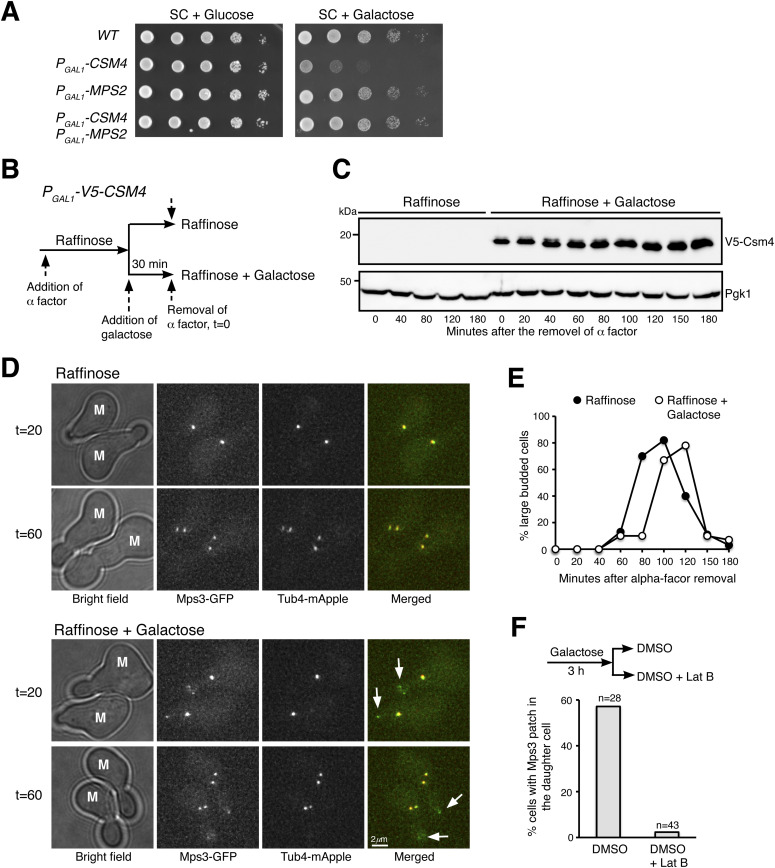
Figure 5. Ectopic production of Csm4 reconstitutes t-LINC complex in mitosis.
(A) Genetic interaction between MPS2 and CSM4. 10-fold diluted yeast cells were spotted onto glucose or galactose medium. Note that ectopic expression of CSM4 in the galactose medium is toxic to the vegetative yeast cell. (B) Schematic diagram showing the experimental procedure for panels (C, D, E). (C) Western blotting showing induced production of Csm4 in the galactose medium. V5-Csm4 was probed by an anti-V5 antibody. The level of Pgk1 serves as a loading control. (D) Formation of the Mps3 patch in the daughter cell in the presence of Csm4. Tub4-mApple (red) marks the spindle pole body. Projected images of 12 z-sections are shown. Arrows point to the Mps3-GFP (green) patch in daughter cells. (E) Quantification of budding index. Cell aliquots were withdrawn at indicated times, and budding morphology was determined by phase-contrast microscopy. More than 200 cells were counted at each time point in both raffinose and galactose treatments. (F) Impact of actin polymerization on Mps3 patch formation. Schematic diagram at the top shows the experimental procedure. Fluorescence microscopy was performed 15 min after the treatments to visualize Mps3-GFP patch formation as in panel (C). Lat B, latrunculin B. M, mother cell; SC, synthetic complete.