Figure 5.
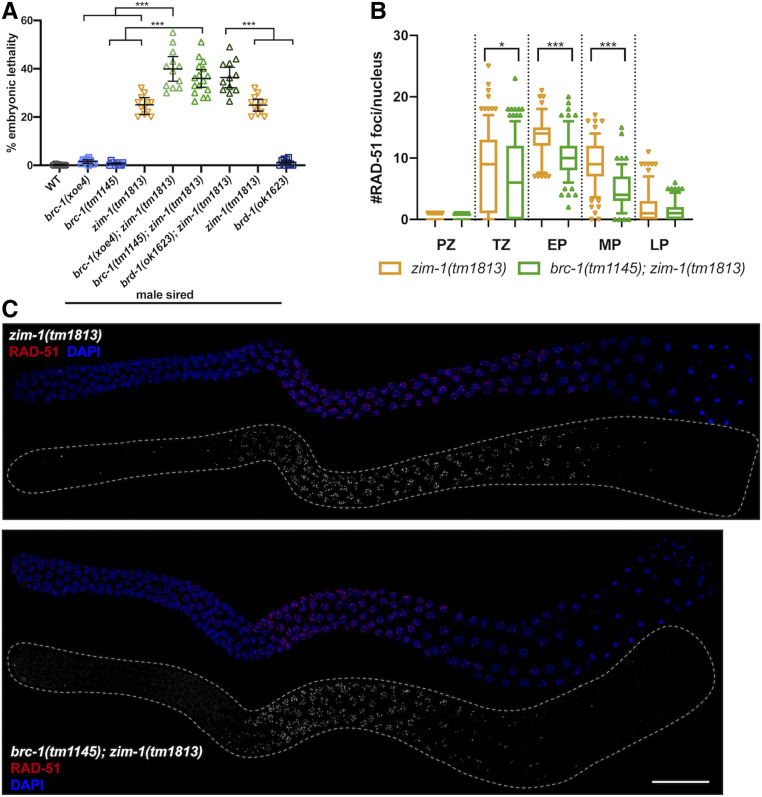
Progeny embryonic lethality is enhanced when sired by brc-1; zim-1 or brd-1; zim-1 double mutant males but RAD-51 stability in not impaired. (A) Embryonic lethality of fog-2(q71) progeny sired by brc-1(xoe4), brc-1(tm1145), zim-1(tm1813), brc-1(xoe4); zim-1(tm1813), brc-1(tm1145); zim-1(tm1813), brd-1(ok1623); zim-1(tm1813), brd-1(ok1623) males. Mean and 95% confidence intervals are shown. The genetic interaction between brc-1 or brd-1 and zim-1 is significant by a one-way ANOVA (***P < 0.0001). A minimum of 10 worms were scored for each genotype. (B) Box whisker plots show average number of RAD-51 foci per nucleus in the different zones. Horizontal line of each box indicates the median, the top and bottom of the box indicates medians of upper and lower quartiles, lines extending above and below boxes indicate SD and individual data points are outliers from 5 to 95%. Statistical comparisons by Mann–Whitney of zim-1(tm1813) vs. brc-1(tm1145); zim-1(tm1813) in the different regions of the germ line: *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.0001. PZ, proliferative zone; TZ, transition zone; EP, early pachytene; MP, mid-pachytene; LP, late pachytene. Numbers of nuclei scored from four germ lines in each zone for zim-1: PZ = 668; TZ = 237; EP = 111; MP = 151; LP = 167 and brc-1; zim-1: PZ = 545; TZ = 318; EP = 155; MP = 137; LP = 149. (C) zim-1(tm1813) and brc-1(tm1145); zim-1(tm1813) mutant germ lines stained with anti-RAD-51 antibody (red) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Images are projections through half of the gonad. A minimum of four germ lines were imaged. Bar, 20 μm.