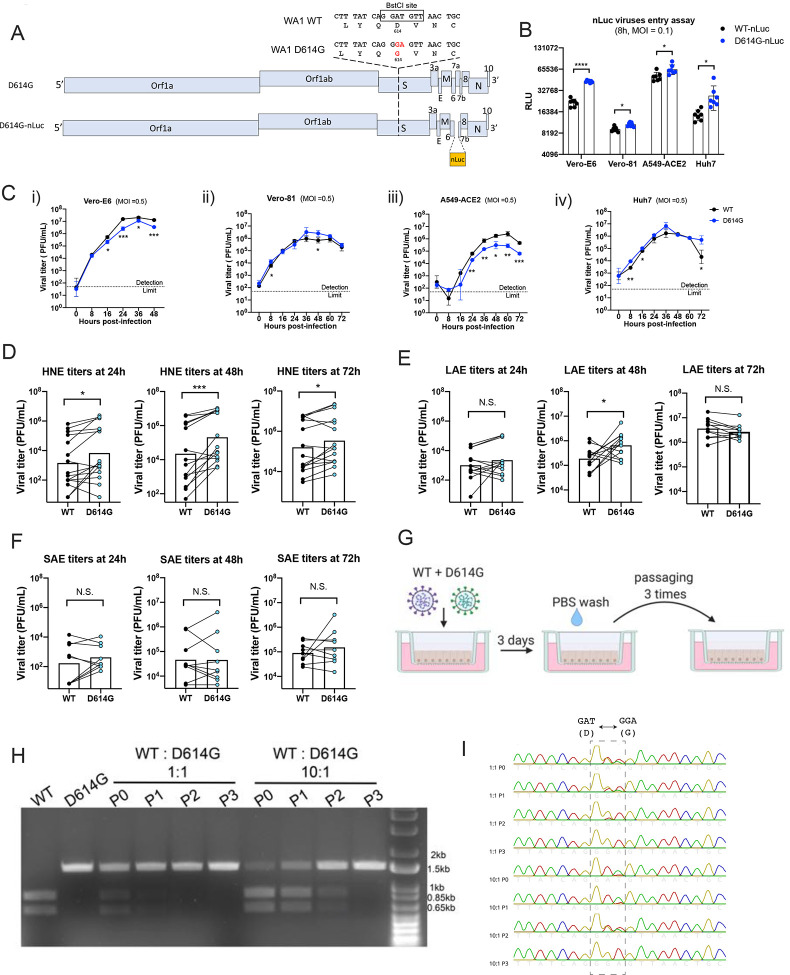
Figure 1. SARS-CoV-2 D614G variant demonstrate enhanced infectivity in some cell lines and replication fitness in upper respiratory epithelia.
A. Genomes of recombinant SARS-CoV-2 D614G variants. B. Entry efficiency of WT-nLuc and D614G-nLuc in multiple cell lines at MOI of 0.1. After 1h infection, cells were cultured in the medium containing neutralization antibodies to minimize the secondary round of infection. The relative light unit (RLU) representing the nLuc expression level was measured at 8h post infection. C. Multi-step growth curves of the two variants at Vero-E6 (i), Vero-81 (ii) and A549-ACE2 (iii) and Huh7 (iv) cell lines at MOI = 0.5. Comparison of 24, 48 and 72h titers between the two variants infected primary nasal (D), large airway (E) and small airway (F) cells in triplicate. Triplicated titers of the two viruses in the cultures form the same donor were analyzed by paired t-test. G. Schematic of competition assay on large airway epithelial cells. Cultures were infected with 1:1 or 10:1 ratio of WT and D614G mixture at MOI at 0.5, and serially passaged three times. H. BstCI digestion of the partial S gene from the competition assay samples. A 1.5kb fragment containing the residue 614 was amplified from the total RNA collected from competition assay. I. Sanger sequencing chromatogram of S RNA collected from the competition assay. Data between the WT and D614G viruses in B and C are analyzed using unpaired t-test, and the data between the two groups in D, E and F are analyzed using paired t-test. N.S., not significantly different, p > 0.05; *, p < 0.05 **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.