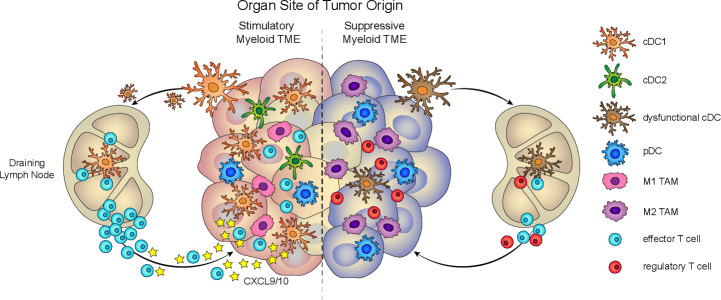
Figure 1.
Tissue-specific myeloid cell composition impacts antitumor immunity. Left, Productive antitumor immunity depends on the presence of stimulatory myeloid cells, such as cDC1, in the TME. cDC1 contributes to several critical functions, such as cross-presentation, antigen transport to the lymph node, T cell priming, and T cell recruitment, to drive tumor-reactive T cell responses. Right, Dysfunctional antitumor immunity can arise from tumors that are predominantly infiltrated by suppressive myeloid cells, such as M2 TAM and functionally impaired DC. cDC, conventional DC; DC, dendritic cell; pDC, plasmacytoid DC; TAM, tumor-associated macrophage; TME, tumor microenvironment.