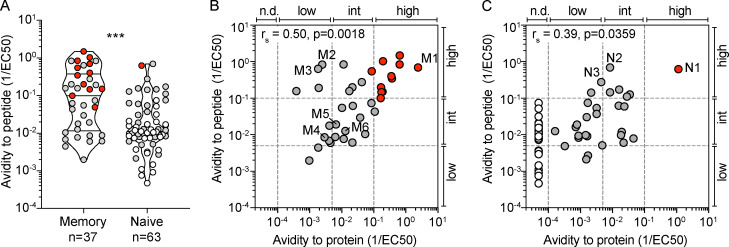
Figure 3.
H1-HA–specific naive and memory CD4+ T cell clones show different functional avidities. Functional avidity of H1-HA–reactive CD4+ T cell clones isolated from donor HD1 was determined by stimulation with titrated doses of synthetic H1-HA peptides or recombinant H1-HA in the presence of autologous monocytes. Proliferation was assessed on day 3 after a 16-h pulse with [3H]thymidine; EC50 values were calculated by nonlinear regression curve fit. Shown are mean data of one experiment done with each clone in duplicate and are representative of three independent experiments. (A) Violin plots of the frequency distribution of reciprocal EC50 values of T cell clones from the memory or naive compartment stimulated with titrated doses of H1-HA peptides. T cell clones specific for the immunodominant H1-HA411–430 epitope are reported as red dots. Lines represent the median and quartiles. ***, P < 0.001 as determined by two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test. (B and C) Scatter plots of reciprocal EC50 values of T cell clones from the memory (B) or naive (C) compartment, stimulated in parallel with recombinant H1-HA (x axis) and synthetic peptides (y axis). EC50 values below the detection limit for stimulations with recombinant H1-HA were set arbitrarily to 20 µg/ml; the corresponding T cell clones are reported as white dots. Spearman correlation was calculated based on EC50 pairs from T cell clones responding to both peptides and recombinant H1-HA (B, n = 36; C, n = 29). Thresholds of functional avidity were set arbitrarily at EC50 values of 10 µg/ml, 200 ng/ml, and 10 ng/ml of antigen. n.d., not detected.