Figure 1. Schematic representation of the scratch assay.
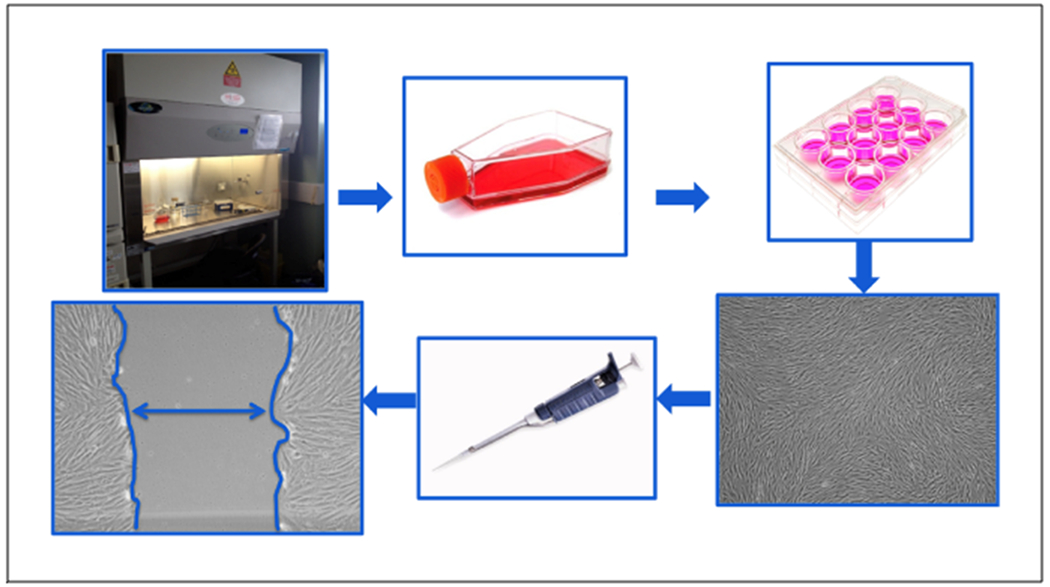
All work is done within an aseptic field to decrease the chance of contamination. Cells are seeded at a desired density in tissue culture flasks and grown in an incubator set to human physiologic conditions (5% CO2, 37° C). Upon reaching a desired confluence, cells are aseptically sub-cultured into 12-well tissue culture plates at a desired seeding density. Cells are grown to 100% confluence in each well of the 12-well plate and scratched using a sterile pipet tip. This “scratch” creates an in vitro mock wound (denoted by double headed arrow), in which cells naturally migrate to close the open area. Each well can be uniquely conditioned and cellular migration rates can be observed and quantified in response to different treatment conditions.
