Figure 3. Arsenic slows cellular migration using the scratch assay.
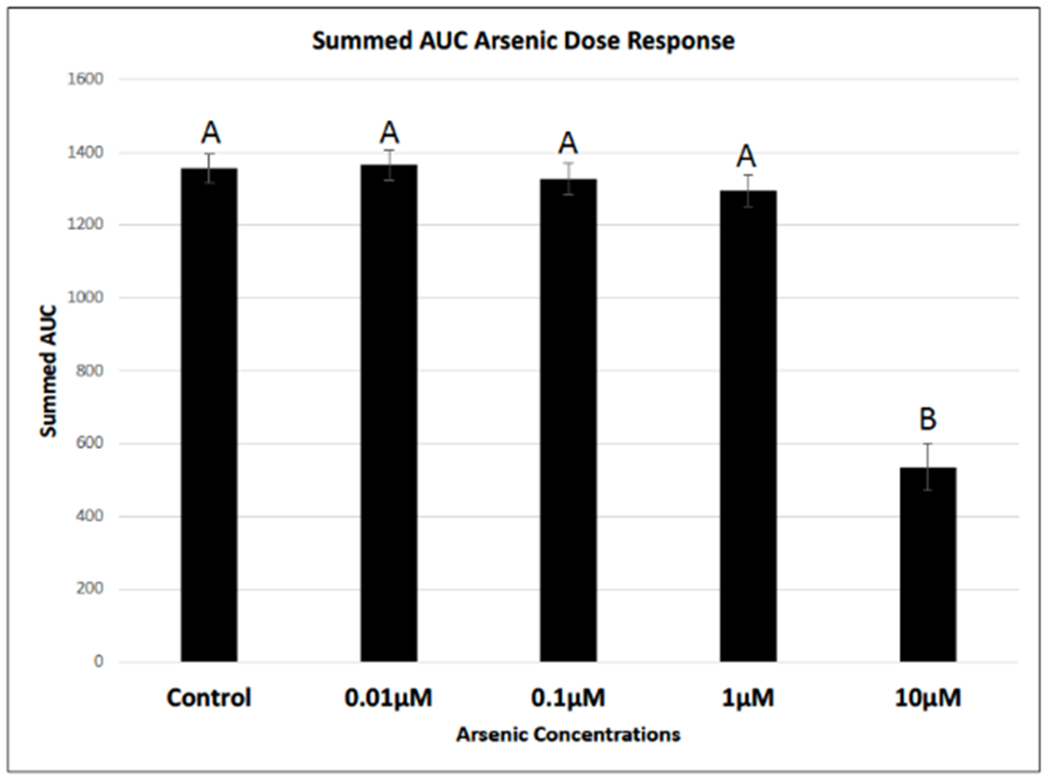
Images were captured over a 24-hour period to observe changes to cellular migration rates in the presence of varying concentrations of arsenic. Raw images were analyzed using an automated MatLab algorithm, which initially measured wound width, then calculated percent closure and finally area under the curve (AUC). 10 μM As treatment group statistically slowed cellular migration of human dermal fibroblasts neonatal (hDFn) compared to all other treatment groups using a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey post-hoc adjustment (p<0.05). Treatments that do not share a common letter are statistically significant from each other (p<0.05).
