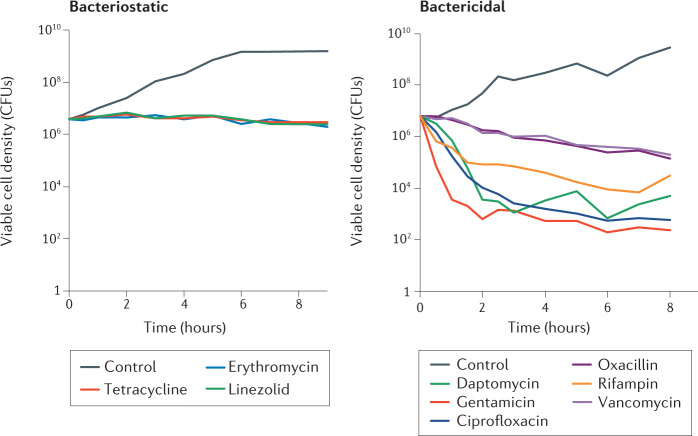
Fig. 1. Killing rates of different antibiotics.
The findings of time–kill experiments measured as changes in the viable cell density of Staphylococcus aureus Newman exposed to 10 times the minimum inhibitory concentration of nine different antibiotics in Mueller–Hinton II medium at 37 °C with aeration are shown. Bacteriostatic antibiotics (left) stop growth and colony-forming units (CFUs) remain stable. By contrast, bactericidal antibiotics (right) kill bacteria and thus the CFUs drop. Of note, a resistant mutant emerged in the culture treated with rifampin, leading to resumed growth at the end of the experiment.