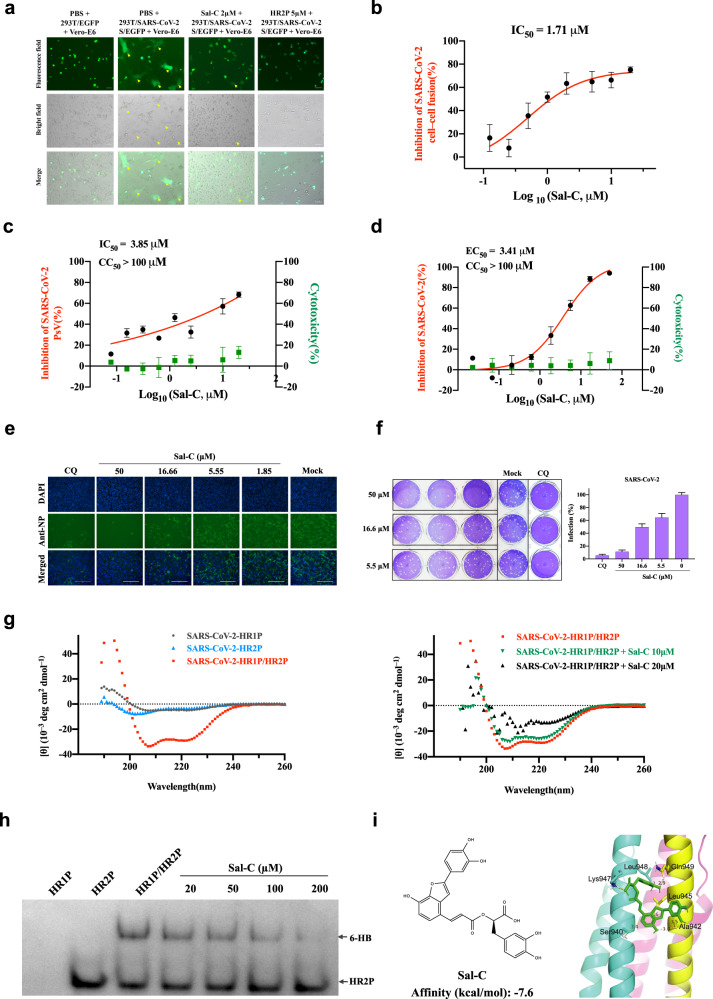
Fig. 1.
Sal-C inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection by blocking the formation of six-helix bundle core of S protein. a SARS-CoV-2 S protein-mediated cell–cell fusion assay. The syncytium of Vero-E6 cells and HEK293T cells with SARS-CoV-2 S overexpression were marked in the pictures. HR2P was used as a positive control. Representative results were shown from three fields were selected randomly each sample with scale bars of 100μm. b Inhibitory activities of Sal-C on SARS-CoV-2 S protein-mediated cell–cell fusion. c Sal-C inhibited the entry of SARS-CoV-2 S PsV on 293T/ACE2 cells. d Validation on the antiviral activity of Sal-C against authentic SARS-CoV-2 in Vero-E6 cells. The inhibitory curve and cytotoxic effect for Sal-C. e The inhibition activity of Sal-C on SARS-CoV-2 infection (green) was detected by indirect immunofluorescence assay. The nuclei (blue) were stained with DAPI, scale bar=200μm. f Plaque reduction assay of Sal-C against authentic SARS-CoV-2 in the Ongoing-infection model. g Sal-C inhibited α-helical conformation change. CD spectra of SARS-CoV-2 HR1P alone (gray), SARS-CoV-2 HR2P alone (blue), and SARS-CoV-2 HR1P/HR2P complex (red) in phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) at 4°C. The typical α-helicity conformation was significantly interfered with Sal-C, as shown in the black and green model, with minimum values at 208 or 222nm. h Determination of the 6-HB between SARS-CoV-2 HR1P and HR2P by 18% N-PAGE. HR1P (25µM) with or without Sal-C were incubated at 25°C for 30min, followed by the addition of HR2P (25µM). The mixture was incubated at 25°C for another 30min before being loaded into the gel. Sal-C reduces the density of the 6-HB. i Chemical structure and schematic diagram of molecular docking between Sal-C and the post-fusion core of 6-HB. The affinity of Sal-C with the post-fusion core of 6-HB was −7.6kcal/mol