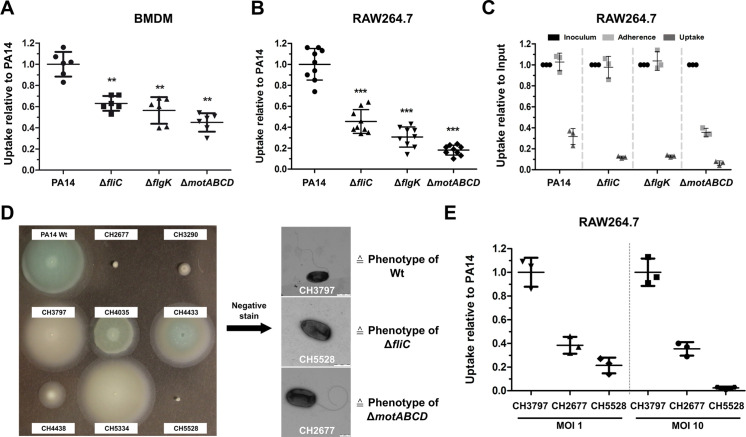
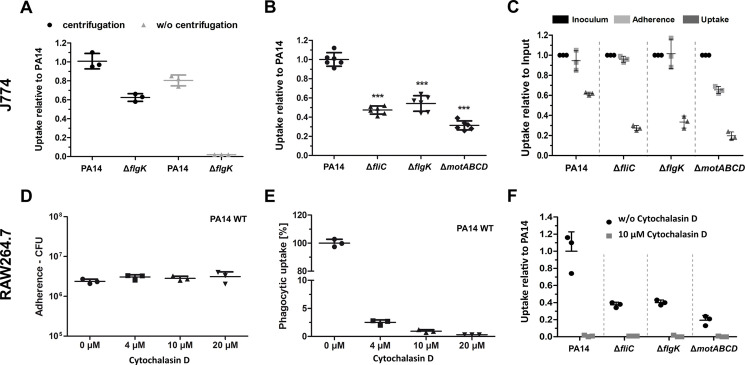
Figure 2. Reduced macrophage uptake of non-flagellated and non-motile P. aeruginosa strains.
Phagocytic uptake 1 hr post infection of PA14 and the three motility variants into bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) (A) and RAW264.7 cells (B) using a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1. The results of at least two independent experiments with three biological replicates are depicted. (C) Adherence of bacterial cells to RAW264.7 macrophages following treatment with 10 µM cytochalasin D to inhibit phagocytic uptake. The initial bacterial load was set to 100% (black, technical replicates) while the bacterial uptake without cytochalasin D is shown as a control. The data of three biological replicates is shown. (D) Left: Representative screen of clinical P. aeruginosa isolates for swimming motility on semi solid agar plates. Right: Analysis of clinical isolates using a negative-staining to identify the presence of flagella. (E) Phagocytic uptake of clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa in RAW264.7 cells 1 hr post infection using an MOI 1 and 10. Mean ± standard deviation of three biological replicates is displayed. **p<0.01; ***p<0.001 in one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (post-hoc test: Dunnett).