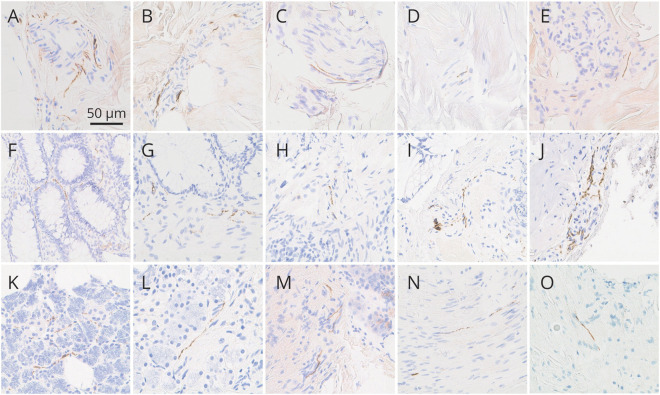
Figure 2. Photomicrographs of skin, colon, and submandibular gland immunohistochemically stained for pathologic α-synuclein with the 5C12 monoclonal antibody-based method.
Photomicrographs of skin (A–E), colon (F–J), and submandibular gland (K–O). All panels show immunoreactivity independently judged by at least 2 of 3 blinded neuropathologists to represent specific positive staining of nerve fibers. Specific positive staining in skin was most often seen in dermal periarteriolar locations (A, B) and within small intradermal nerve fascicles (C, D) and less often adjacent to sweat glands (E). Specific positive staining was present in the lamina propria of the mucosa (F, G) but more often in submucosal nerve fibers (H–J), sometimes in periarteriolar locations (J). Specific positive staining in submandibular gland was seen both in the glandular parenchyma (K, L) and stroma (M–O); in stroma, it was often localized to nerve fascicles (N, O). The calibration bar in (A) serves for all panels.