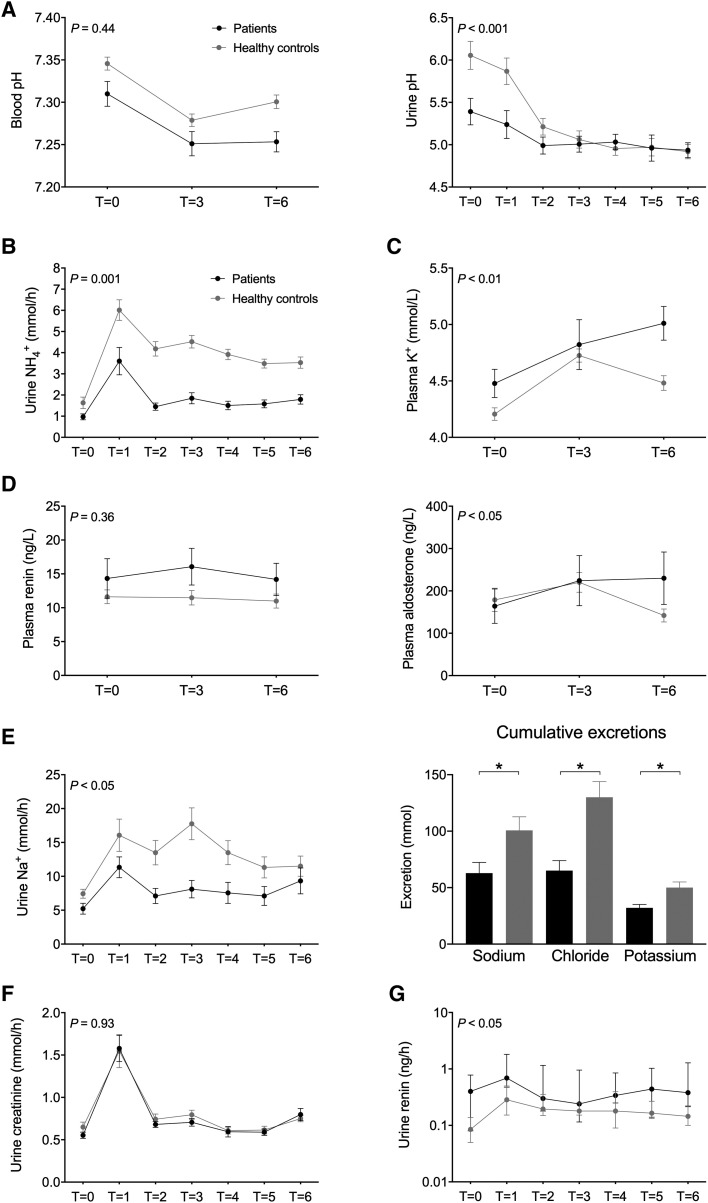
FIGURE 1.
Effects of an acute acid load with ammonium chloride on (A) venous blood pH and urine pH, (B) urine ammonium excretion, (C) plasma potassium (K+), (D) plasma renin and aldosterone, (E) urine sodium excretion and cumulative excretion of sodium, chloride and potassium, (F) urine creatinine excretion and (G) urine renin excretion. Group comparison was performed using repeated measures two-way analysis of variance reporting the P-value for interaction. Cumulative excretions were compared with unpaired t-tests. Urine renin was not normally distributed and was therefore log-transformed for analysis.