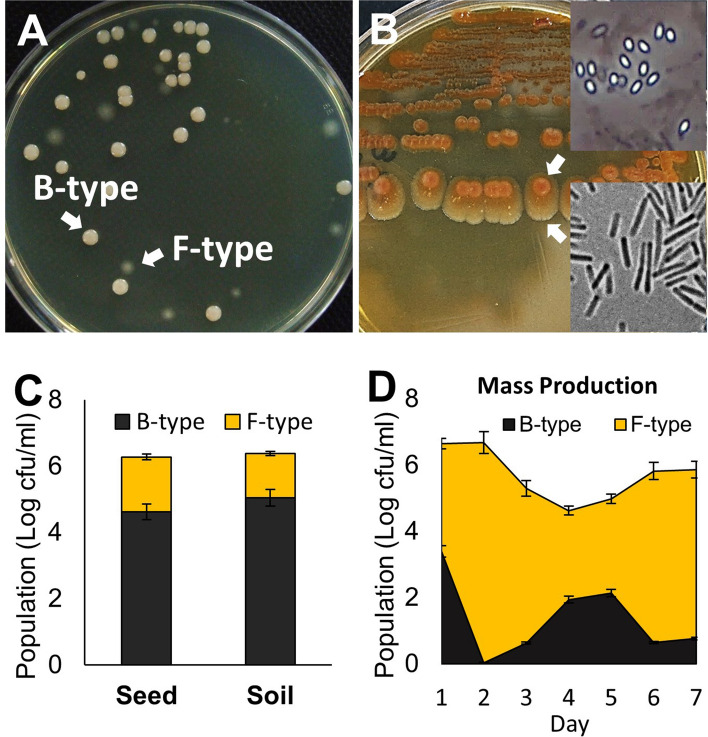
Figure 1.
Phenotypic variation of P. polymyxa in culture. (A) Cells in 4-day-old TSB culture formed two distinct types of colonies, termed as B (wild-type) and F (variant) types when plated on TSA and incubated at 28 °C for 2 days. (B) Phenotypic variation was also observed when cells in B-type colonies were streaked on TSA plates and cultured at 37 °C for 10 days. The production of endospores was observed at the center of the colony using a phase-contrast microscope. The outermost region of this colony lacks endospores. (C) The phenotypic variation observed on cucumber seedlings when they were treated with B-type cell suspensions (106 cfu/mL) via seed coating or soil treatment methods and incubated for 11 days at 28 °C. (D) The proportion of B- and F- type cells were determined during a large scale culture under the conditions employed for commercial biocontrol production preparation. After inoculating 1.5 L of 48-h-old culture initiated using B-type cells into 250 L fermenter containing a medium used for preparing industrial biocontrol products, samples taken every day for 7 days were analyzed.