Figure 1.
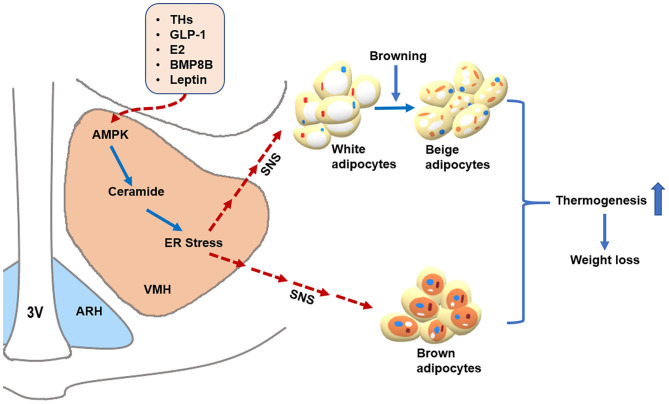
AMPK within the VMH regulates BAT thermogenesis and WAT browning. Peripheral signals, such as THs, GLP-1, E2, BMP8B, and leptin, may act on the VMH to inhibit AMPK, which subsequently promotes BAT thermogenesis and WAT browning through activating the SNS, resulting in body weight loss. Additionally, THs and E2 may decrease ceramide and ER stress levels by suppressing AMPK in the VMH, leading to enhanced thermogenesis via the SNS. Alleviating ER stress in the VMH also increases hypothalamic leptin sensitivity. Whether ceramide and ER stress can mediate the thermogenic effects of GLP-1 and BMP8B warrant further investigation. The solid blue arrows represent activation, the dotted red arrows represent inhibition. 3V: third ventricle. ARH: arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. VMH: ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus. AMPK: adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase. ER stress: endoplasmic reticulum stress. SNS: sympathetic nervous system. THs: thyroid hormones. GLP-1: glucagon-like peptide-1. E2: estrogens. BMP8B: Bone morphogenetic protein 8B.