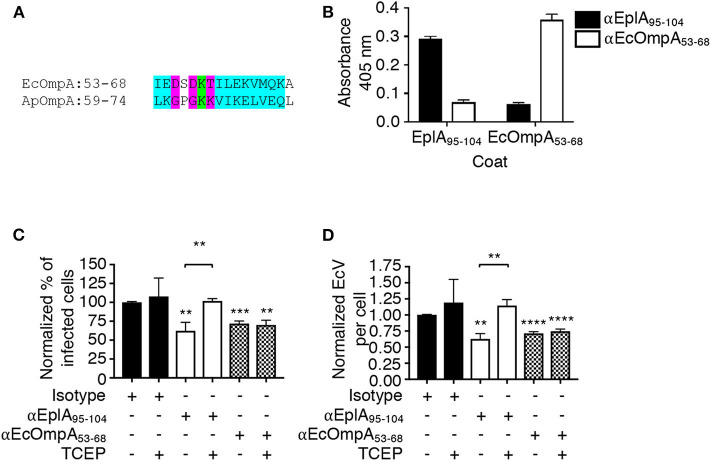
Figure 7.
EplA residues 95-104 are key for E. chaffeensis to co-opt host cell surface PDI thiol reductase activity. (A) Alignment of the ApOmpA59−74 receptor binding domain with EcOmpA53−68. Green highlighting denotes identical amino acids. Turquoise highlighting demarcates highly similar amino acids as defined by Clustal Omega. Magenta highlighting signifies amino acids that are weakly similar. (B) ELISA in which EplA95−104 and EcOmpA53−68 antibodies were used to screen wells coated with peptides corresponding to EplA95−104 and EcOmpA53−68. Each antiserum only recognized the peptide against which it had been raised. (C,D) E. chaffeensis DC organisms were treated with rabbit preimmune serum or rabbit antiserum (α) specific for EplA95−104 or EcOmpA53−68 followed by incubation with THP-1 cells in the continued presence of antiserum with or without TCEP. The host cells were examined 24 h later by fluorescence microscopy for the percentages of infected cells (C) and numbers of EcVs per cell (D). Data are presented as the mean values ± SD from triplicate samples and are representative of experiments performed three separate times. Statistically significant values are indicated. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. Asterisks above columns indicate statistically significant differences in levels of infection relative to the results for preimmune serum-treated cells. Asterisks over the brackets denote a statistically significant difference between the levels of infection of EplA95−104 antiserum-treated DCs following incubation with or without TCEP.