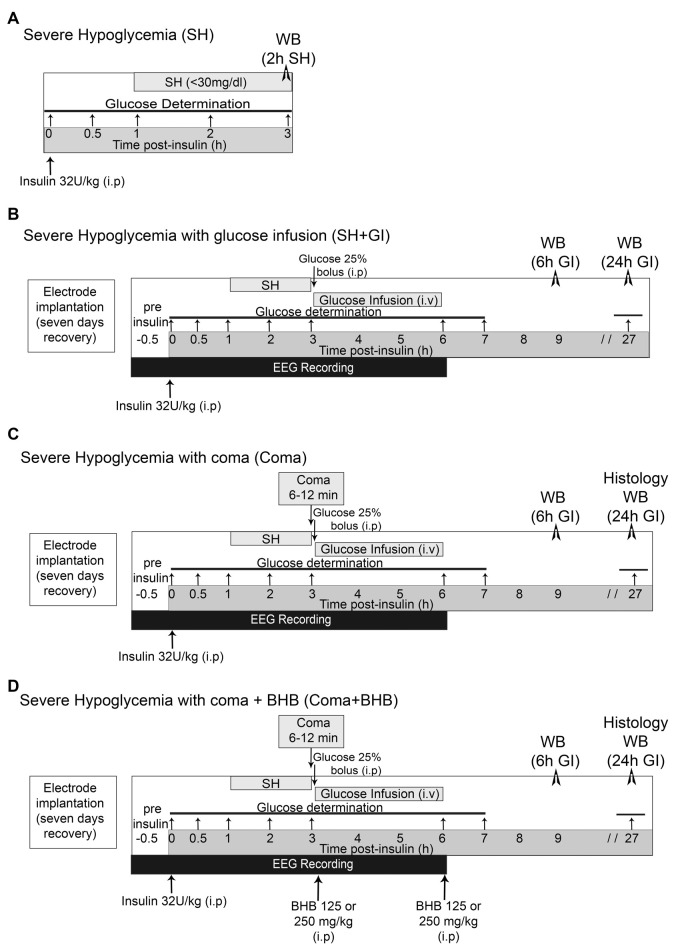
Figure 1.
Induction severe hypoglycemia and the hypoglycemic coma. (A) Severe hypoglycemia (SH) group. SH was induced by the intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of insulin (32 U/kg) and animals were euthanized 2 h after they reached 30 mg/dl blood glucose. (B) SH + GI group. Animals were implanted with electrodes 1 week before the induction of hypoglycemia for electroencephalogram (EEG) recording and were subjected to SH with glucose infusion (GI). Insulin was injected (i.p) and 2 h after animals reached SH, they were rescued with glucose before they fell into the coma state. (C) Coma group. Animals were treated identically as those from the SH + GI, but SH was left to progress to the coma state for 6–12 min and immediately after they were rescued with glucose. (D) Coma + BHB group. Animals were treated identically as the Coma group, but they received two doses of either 125 or 250 mg/kg D isomer of β-hydroxybutyrate (D-BHB; i.p.), the first 10 min after the onset of glucose infusion after the coma and the second at the end of glucose infusion glucose infusion. Animals were euthanized 6 or 24 h after GI in groups (B–D).