Figure 2. Initiators of coagulation.
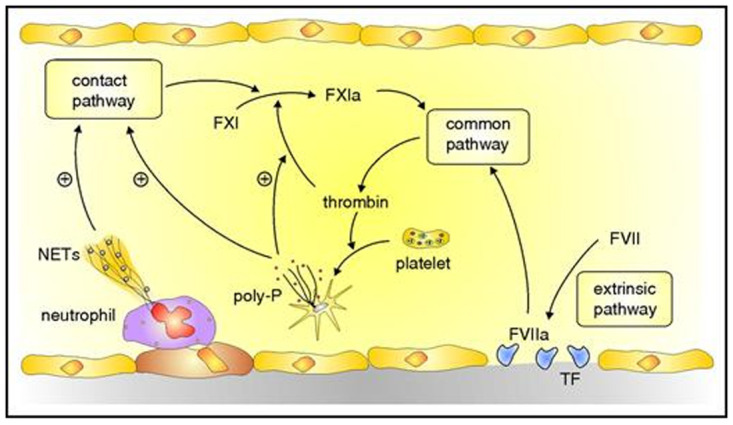
Coagulation is initiated by the extrinsic pathway when tissue factor (TF) exposed at sites of vascular injury binds and activates factor (F) VII. The FVIIa–TF complex activates FX in the common pathway to generate prothrombinase, which generates thrombin. Additional activation of coagulation occurs when thrombin-activated platelets release polyphosphate (poly-P) and activated neutrophils extrude DNA and RNA to form neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). NETs and poly-P activate the contact pathway, which yields FXIa and leads to additional thrombin generation via the common pathway. Poly-P amplifies this pathway by promoting thrombin-mediated activation of FXI. Figure and legend reproduced with permission from the American Society of Hematology 18.
