Figure 5.
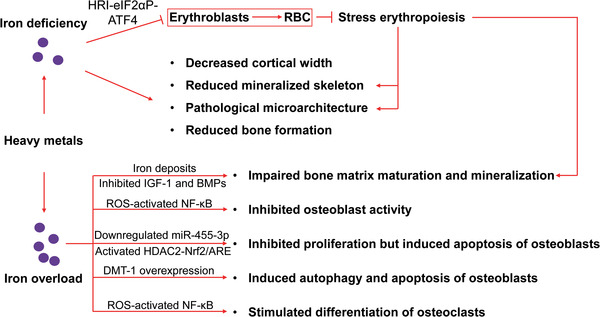
Mechanisms underlying the bone damage mediated by iron deficiency and iron overload. Both iron deficiency and iron overload can cause detrimental effects on bone metabolism upon heavy metal exposure. The HRI‐eIF2αP‐ATF4 signaling pathway might be involved in bone damage under iron deficiency via regulation of stress erythropoiesis. Dysregulated hepcidin, BMP, and IGF signaling pathways could be involved in bone damage observed under iron overload. The induction of oxidative stress, dysregulated microRNA and histone deacetylation by iron overload could contribute to dysregulated osteogenesis and osteoblastogenesis. RBC, red blood cell; ROS, reactive oxygen species; DMT‐1, divalent metal transporter 1; IGF‐1, insulin‐like growth factor 1; BMPs, bone morphogenetic proteins.
