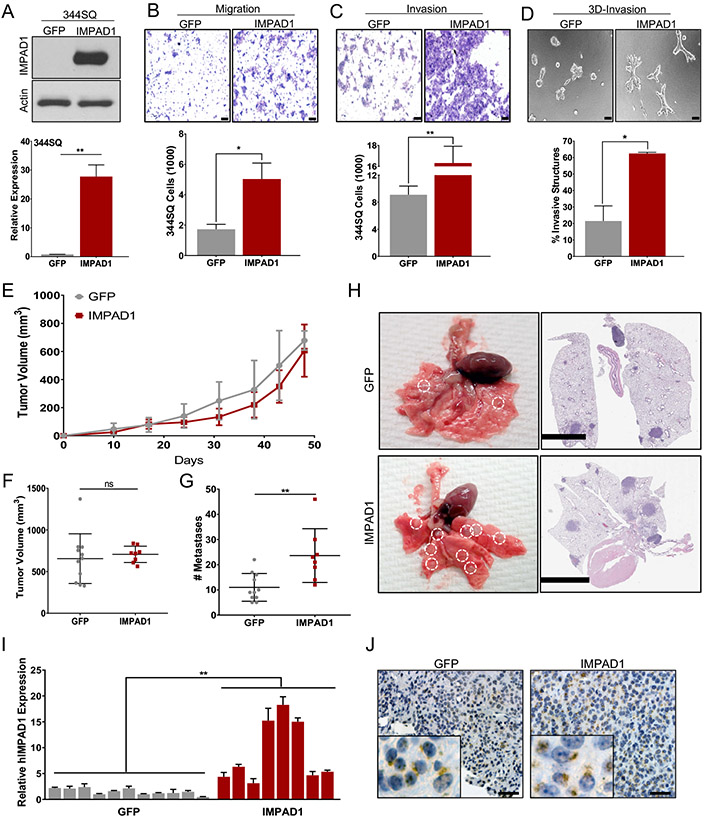
Figure 2. IMPAD1 expression is sufficient to drive lung cancer invasion and metastasis.
a. RT-qPCR and western blot analysis for human IMPAD1 expression in 344SQ cells with stable overexpression compared to GFP control. b-c. 344SQ cells overexpressing IMPAD1 show a significant increase in (b) migration and (c) invasion compared to GFP controls (scale bar: 100uM). d. IMPAD1 overexpressing cells form significantly more invasive structures compared to GFP in 3D matrix comprising of 1.5 mg/ml Collagen in Matrigel by day 6 (scale bar: 100uM). e-f. Primary tumor growth for 344SQ GFP (n=11) and IMPAD1 (n=8) overexpressing cells implanted subcutaneously into syngeneic mice (e) over time, and (f) at time of euthanasia. g. IMPAD1 overexpressing cells form significantly more lung metastatic nodules compared to GFP control. h. Representative lungs and their respective H&E stained sections showing increased metastases in lungs from mice implanted with IMPAD1 overexpressing cells compared to control (scale bar 5mM). i-j. Analysis to confirm overexpression of IMPAD1 in SQ tumors by (i) RT-qPCR for RNA, and (j) immunohistochemistry for protein (scale bar: 20uM). See also Supplemental Fig. S4. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Significance by Student’s T-test. P-value<0.05 - *; <0.002 - **