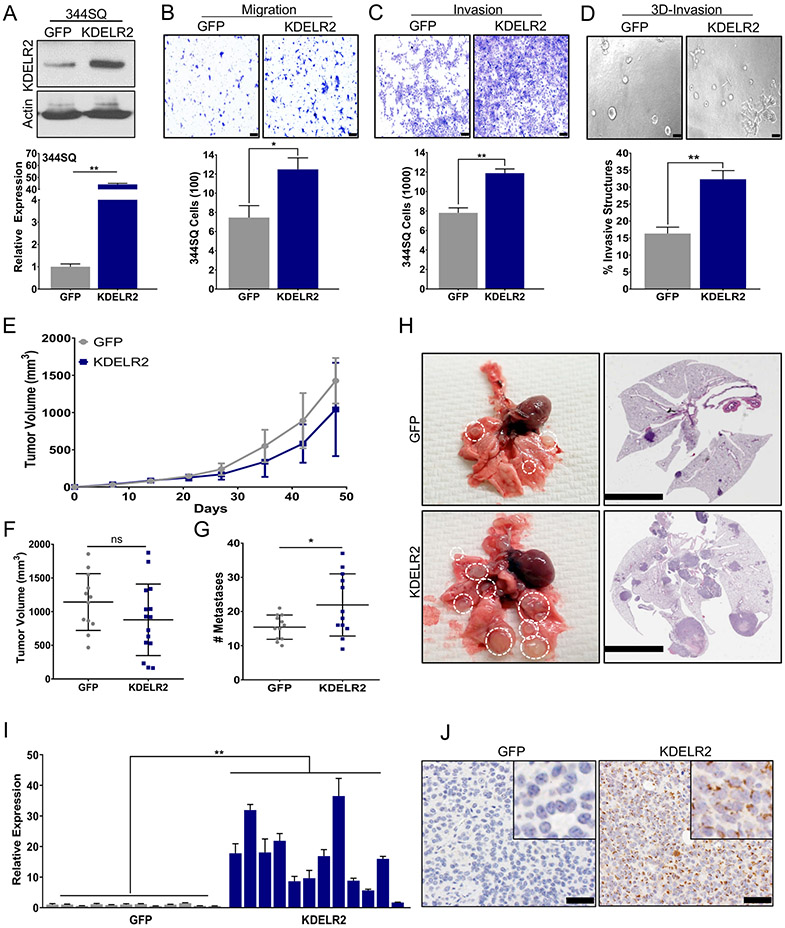
Figure 3. KDELR2 expression is sufficient to drive lung cancer invasion and metastasis.
a. RT-qPCR and western blot analysis for mouse KDELR2 expression in 344SQ cells with doxycycline-inducible overexpression compared to GFP control after 24-hour induction. b-c. 344SQ cells overexpressing Flag-tagged KDELR2 show a significant increase in (b) migration and (c) invasion compared to GFP after 24-hour induction (scale bar: 100uM). d. KDELR2 overexpressing cells pre-induced for 24 hours before seeding form significantly more invasive structures compared to GFP in 3D matrix comprising of 1.5 mg/ml Collagen in Matrigel by day 6 (scale bar: 100uM). e-f. Primary tumor growth for 344SQ GFP and KDELR2 inducible cells implanted subcutaneously in syngeneic mice (e) over time, and (f) at time of euthanasia. N=12. g. KDELR2 overexpressing cells form significantly more lung metastatic nodules compared to GFP control. h. Representative lungs and their respective H&E stained sections showing increased metastases in lungs from mice implanted with KDELR2 overexpressing cells compared to GFP control (scale bar: 5mM). i-j. Analysis to confirm overexpression of Flag-tagged KDELR2 in SQ tumors by (i) RT-qPCR for RNA, and (j) Flag IHC for protein (scale bar: 50uM). See also Supplemental Fig. S5. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Significance by Student’s T-test. P-value<0.05 - *; <0.002 - **