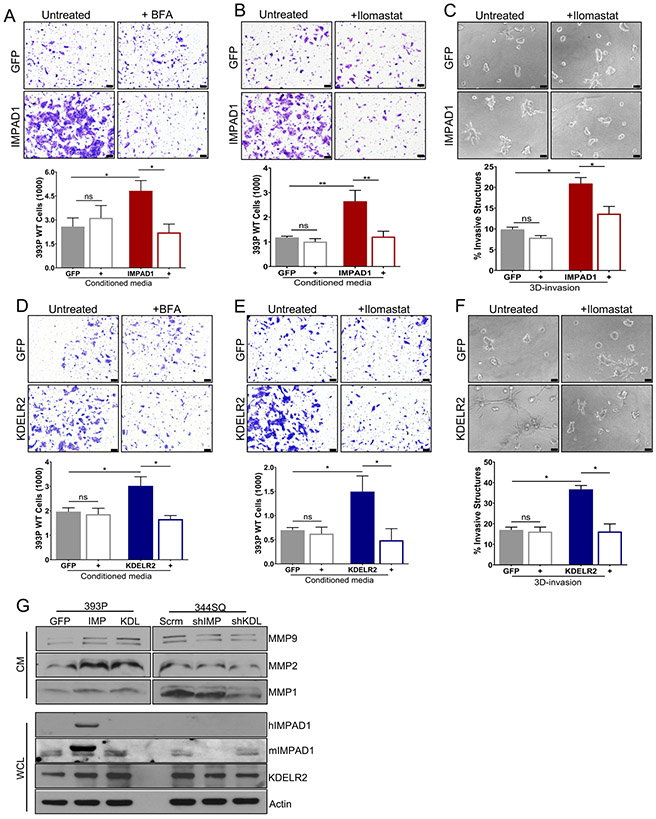
Figure 6. IMPAD1 and KDELR2 independently induce Golgi-mediated secretion of proteases such as MMPs to drive lung cancer cell invasion.
a-b. Conditioned media from inducible IMPAD1 overexpressing cells significantly increase invasiveness of non-invasive 393P WT cells. This phenotype is reversed, when using conditioned media from inducible IMPAD1 overexpressing cells after treatment with (a) BFA, a Golgi secretion inhibitor (1uM 6 hours) or when conditioned media from IMPAD1 overexpressing cells was supplemented with (b) Ilomastat, an MMP inhibitor (1uM). c. Invasive structures formed by cells with inducible overexpression of IMPAD1 or GFP control, in matrix comprising of 1.5mg/ml collagen in Matrigel, upon inhibition of MMPs with Ilomastat (1uM) (day 5). d-e. Conditioned media from dox-inducible KDELR2 overexpressing cells is sufficient to promote invasiveness of non-invasive 393P WT cells. This phenotype is rescued, when using conditioned media from inducible KDELR2 overexpressing cells after treatment with (d) BFA (1uM 6 hours), or when conditioned media from KDELR2 overexpressing cells was supplemented with (e) Ilomastat (1uM). f. Invasive structures formed by cells with inducible overexpression of KDELR2 or GFP control, in matrix comprising of 1.5mg/ml collagen in Matrigel, upon inhibition of MMPs with Ilomastat (1uM) (day 5). Scale bar for all images:100uM. g. Western blot analysis of conditioned media (CM) collected from human IMPAD1 and mouse KDELR2 overexpressing and knockdown cells shows IMPAD1- and KDELR2-regulated secretion of MMPs 1, 2, and 9. Whole cell lysate (WCL) collected from the same cells confirms IMPAD1 and KDELR2 overexpression and knockdown. See also Supplemental Fig. S9. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Significance by Student’s T-test. P-value<0.05 - *; <0.002 - **