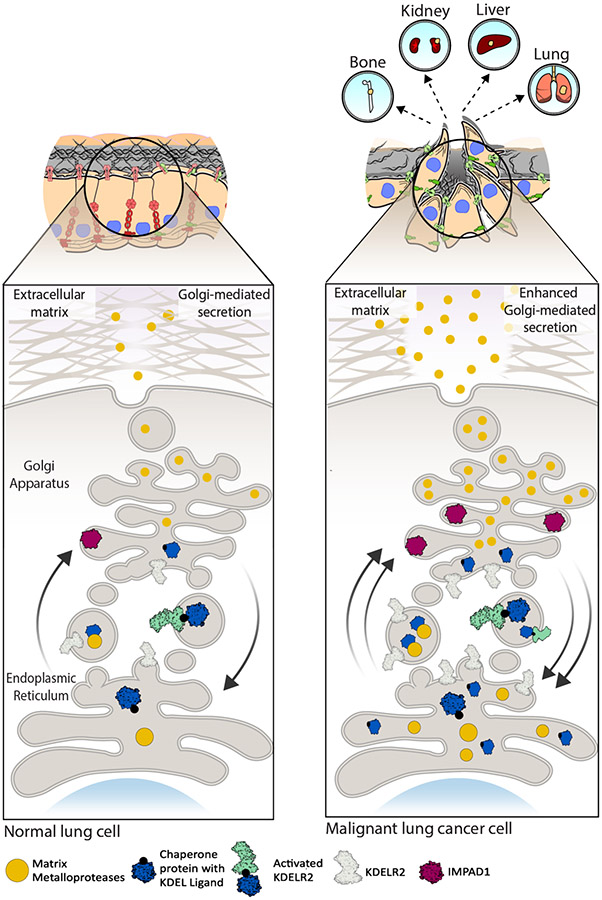
Figure 7. Working model for IMPAD1 and KDELR2 as part of the Golgi secretory cascade that regulate secretion of MMPs to drive NSCLC invasion and metastasis.
Cargo (secretory) proteins such as matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) in the ER bind to the chaperone proteins a with KDEL ligand. This leaves KDELR2 inactive during anterograde transport. Once in the Golgi, MMPs dissociate from the chaperone protein and are secreted into the ECM, whereas chaperone proteins bind to KDELR2 thus activating it during retrograde transport. IMPAD1 is localized to the Golgi and is involved in secretion of proteases like MMPs. Normal function of IMPAD1 and KDELR2 as part of the ER-Golgi secretion pathway in non-malignant lung cell lead to regular Golgi-mediated secretion. Increased IMPAD1 and KDELR2 expression in aggressive, metastatic lung cancer cells lead to hyperactive Golgi-mediated secretion of MMPs, thereby enhancing ECM degradation and promoting metastatic NSCLC.