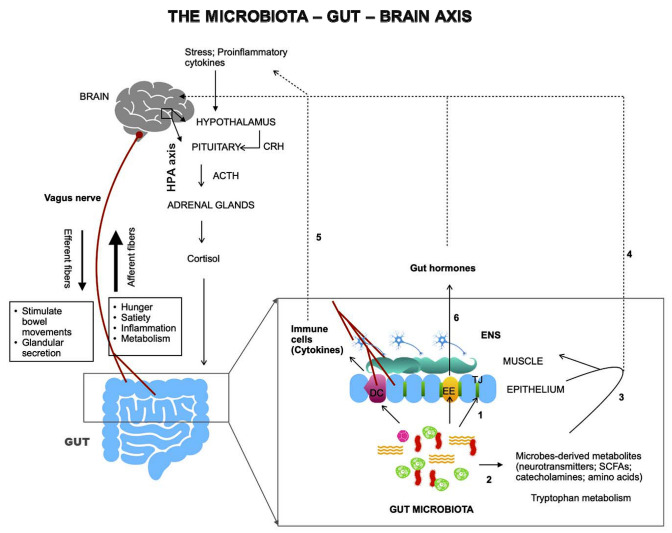
Fig. 1.
Microbiota and the gut-brain axis. The gut-brain axis forms a bidirectional network involving three major pathways—the neural pathway (vagus nerve, enteric nervous system), the immune pathway (cytokines) and the endocrine pathway (HPA axis, gut hormones). Gut microbiota modulates this axis via numerous direct and indirect ways (1–6, as described in the text). HPA hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, EE enteroendocrine cells, DC dendritic cells, TJ tight junctions, SCFAs short chain fatty acids. Bold arrows: local interactions; dashed arrows: via circulation