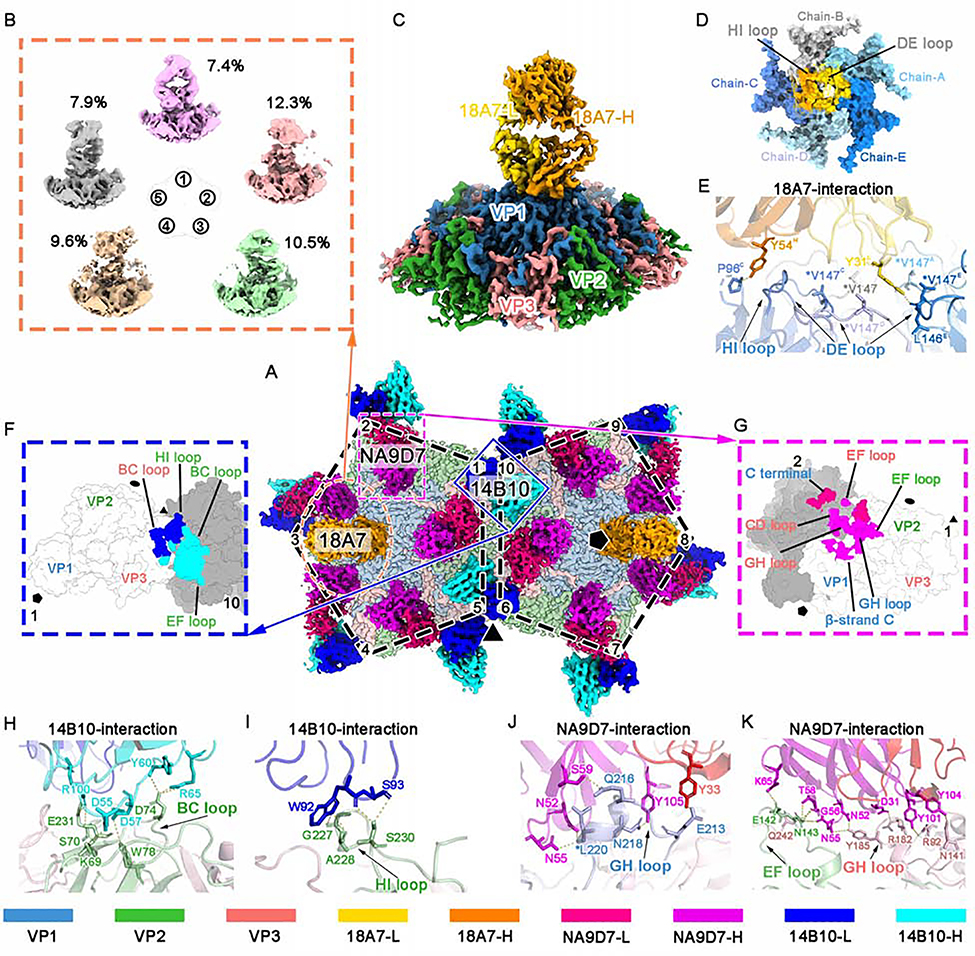
Figure 3. Sub-particle reconstruction of the CVA16-M:18A7 immune complex and interaction analysis of CVA16-M:18A7, CVA16-M:14B10, and CVA16-M:NA9D7.
(A) Surface view of the cryo-EM densities of two adjacent five-fold vertexes of CVA16-M:18A7:14B10:NA9D7, containing 10 asymmetric units. Fabs bound to these ten asymmetric units include two 18A7 Fabs (orange), 10 14B10 (heavy chain: cyan, light chain: cyan) and 10 NA9D7 (heavy chain: magenta, light chain: red). Icosahedral 2-, 3-, and 5-fold axes are indicated by black ellipse, triangle, and pentagon symbols, respectively.
(B) Sub-particle reconstruction of the CVA16-M:18A7 five-fold vertex yielded five well-defined 3D classes from different number of sub-particles (percentages indicated) showing different Fab binding directions.
(C and D) Surface views of the final sub-particle reconstruction of the five-fold vertex showing CVA16-M:18A7 binding (resolution 3.67 Å) viewed from side (C) and top (D). In d, the Fab density is removed to reveal the footprint of Fab 18A7 on a surface area buried by the Fab heavy (gold) and light (orange) chains.
(E) Close-up of the interface between the capsid and Fab 18A7 with residues participating in the interactions labeled and their side chains shown as sticks on the ribbon models.
(F and G) Footprints of Fabs 14B10 (F) and NA9D7 (G) on the CVA16 viral capsid rendered as surface representation.
(H and I) Close-up views of the interface between the capsid and either the heavy (H) or the light chain (I) of Fab 14B10.
(J and K) Fab NA9D7 interacts with the GH loop of VP1 (J), the EF loop of VP2, and the GH loop of VP3 (K). Hydrogen bonds and salt bridges are marked by yellow dashed lines. Side chains involved in the interaction between the antigen and the antibody are labeled and shown as sticks. Asterisks mark the position of an escape mutation.
Proteins are colored according to the codes at the bottom.
See also Figures S3 and S5 and Table S1.