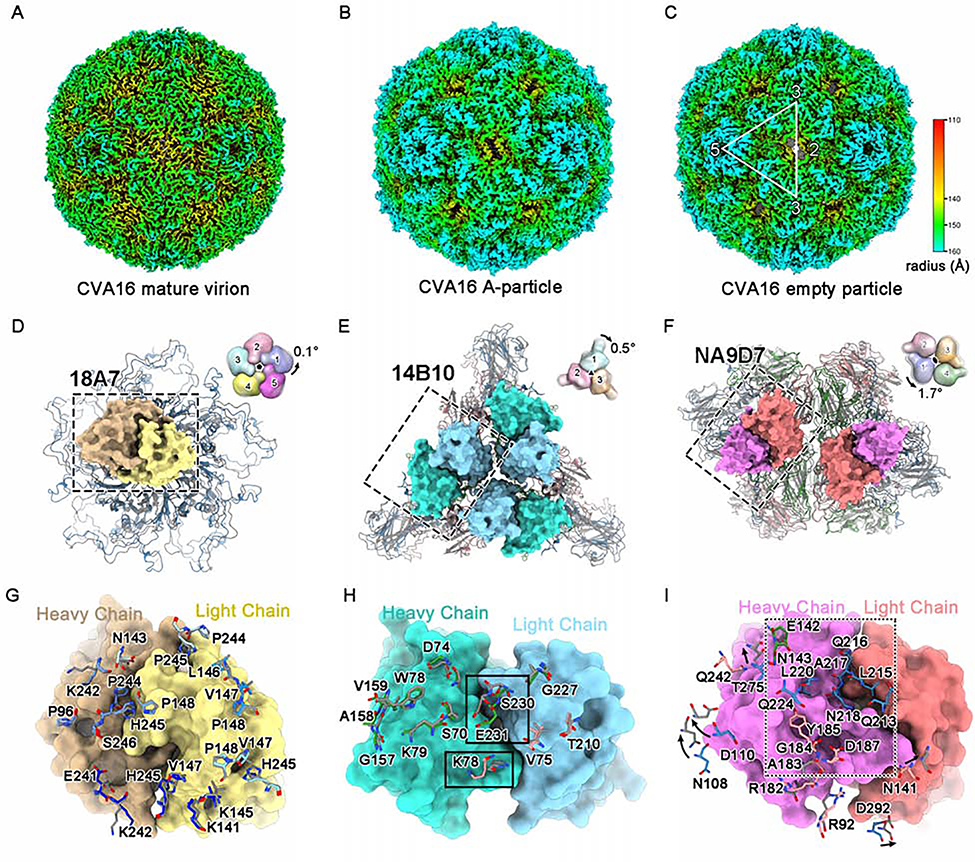
Figure 4. Structural and antigenic comparisons among different types of CVA16 particles.
(A-C) Radially colored surface views of the cryo-EM density maps of the CVA16 mature virion (A), A-particle (B) and empty particle (C).
(D-F) Structural comparisons of the mature virion and A-particle (which is highly similar to the empty particle) on their viral 5-fold (D), 3-fold (E) and 2-fold (F) vertexes, respectively. The variable regions of one 18A7 Fab (heavy chain: orange, light chain: yellow), three 14B10 Fabs (heavy chain: cyan, light chain: light blue) and two NA9D7 Fabs (heavy chain: magenta, light chain: pink) bound to the viral 5-fold (D), 3-fold (E) and 2-fold (F) vertexes are shown as surfaces. Diagrams in the upper-right corner depict the structural discrepancy for different protomers located in 5-fold, 3-fold, or 2-fold vertexes, with global rotation against the corresponding icosahedral axes between the mature virion (colored) and the A-particle (gray, 50% transparency). The axes are located at the center of the diagrams and are perpendicular to the page.
(G-I) Close-up views and structural comparisons of the binding sites of 18A7 (G), 14B10 (H), and NA9D7 (I) between the mature virion and the A-particle. The 18A7 binding sites cover five VP1s localized to the 5-fold vertex of the viral capsid (blue) (G). (H) Important differences in the residues between the mature virion and A-particle (rectangle). (I) NA9D7 epitope residues of the mature virion that were not interpreted in the A-particle model are boxed in the dashed rectangle. VP1, VP2, VP3, and VP4 of the CVA16 mature virion are colored blue, green, red, and yellow, respectively. The A-particle model is in gray. The amino acid residues of CVA16 involved in nAb-capsid interactions in (G-I) are shown as sticks.
See also Figure S6.