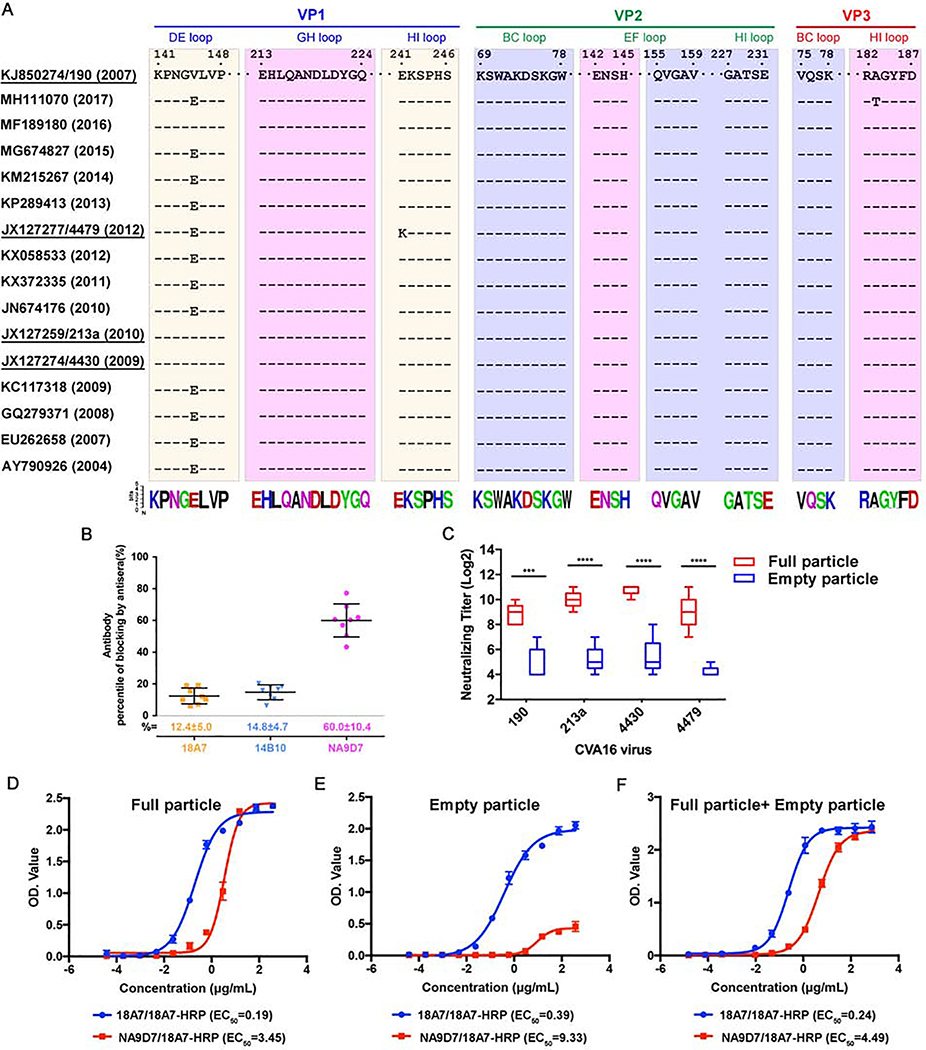
Figure 5. Conservation analysis of neutralization epitopes and ELISA of purified CVA16 particles.
(A) Sequence alignment showing the epitopes of the three Fabs covering 16 strains of CVA16. The neutralization epitopes are boxed as cream (18A7), purple (14B10) and pink (NA9D7), respectively. The amino acid residue conservation is depicted beneath the boxes using the Weblogo representation of the alignment of 157 CVA16 strains.
(B) Competitive ELISA of 18A7, 14B10, and NA9D7. Antibodies were conjugated to HRP and then used to block the binding of CVA16-positive human sera to CVA16 particles that were pre-coated on ELISA plates. The percentage of blockage is expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD).
(C) Cross-strain in vitro neutralizing efficacies of antisera elicited by different types of CVA16 particles. BALB/c mice were vaccinated intraperitoneally with CVA16 strain 190 full particles or empty particles. The neutralizing efficacies of the antisera collected from mice against CVA16 strains 190, 213a, 4430, and 4479 were evaluated by neutralization assay, with neutralizing titers expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was analyzed by an unpaired Student’s t-test (***P < 0.001, n=5).
(D-F) Reactivities of CVA16 particles by two modes of double-antibody sandwich ELISAs. The ELISA systems used 18A7 paired with 18A7-HRP or 18A7 paired with NA9D7-HRP as the capture and detection antibody for the detection of plenary particles and mature virions, respectively. CVA16 full particle (D), empty particle (E) and 1:1 mixture (F) were tested in the two ELISA systems. EC50 values were calculated with curves generated by nonlinear regression fitted.