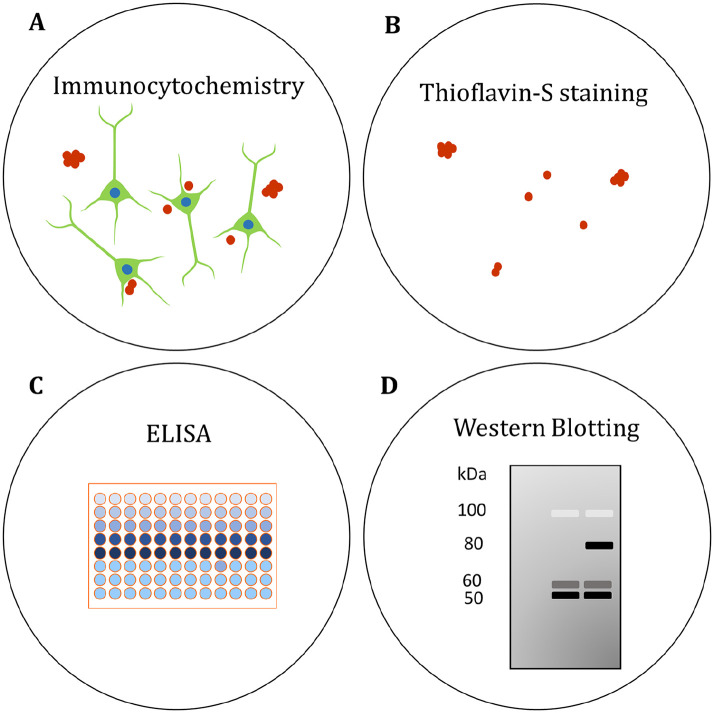
Figure 5.
Assessing Aβ and tau pathology in human brain organoids. (A) The localization of Aβ and phosphorylated tau (p-tau) has been visualized in organoids by immunocytochemistry (Choi and others 2014; Gonzalez and others 2018; Lee and others 2016; Lin and others 2018; Park and others 2018; Pavoni and others 2018; Raja and others 2016). (B) β-sheet aggregates have been stained with the fluorescent Thioflavin-S (Thio S) dye. Thio S staining was proposed to identify tau pathology in AD organoids (Raja and others 2016), though the precise molecular identity of the aggregates needs to be confirmed. (C) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) have been used to quantify secreted Aβ in the organoid medium (Choi and others 2014; Gonzalez and others 2018; Lee and others 2016; Lin and others 2018; Park and others 2018; Pavoni and others 2018; Raja and others 2016). (D) Protein levels of Aβ and p-tau have been compared in AD and control organoids by western blotting semiquantitative analysis (Choi and others 2014; Gonzalez and others 2018; Lin and others 2018; Park and others 2018; Raja and others 2016). See also Table 1.