Figure 1 ∣. Genome-wide CRISPR screen for genetic interactors of C9ORF72.
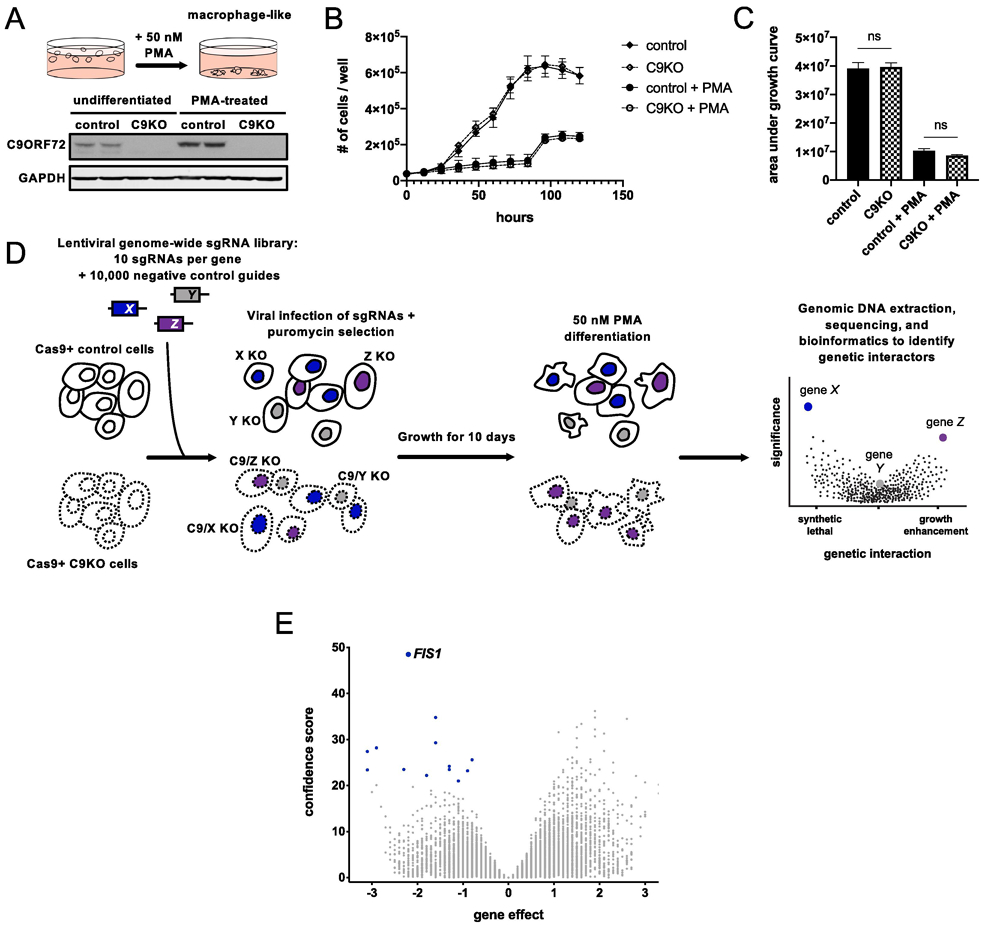
(A) PMA treatment differentiates U937 cells into adherent, macrophage-like cells. Detection of C9ORF72 protein levels by immunoblot in undifferentiated or PMA-treated Cas9+ U937 cells infected with a control or C9ORF72-targeting sgRNA. (B) Growth curves for control or C9KO U937 cells ± PMA. Values represent mean ± s.e.m. of n=3 replicate wells. (C) Analysis of growth quantified with area under the curve metric. Control and C9KO cells grow similarly, with (two-tailed unpaired t test; ns p=0.8537) or without PMA (two-tailed unpaired t test; ns p=0.1170). (D) Schematic of CRISPR screening approach to identify genetic interactors of C9ORF72. (E) Volcano plot of all genes indicating casTLE effect and confidence scores for genome-wide screen in PMA-treated U937 cells, with n=2 replicate screens. Gene effect indicates the magnitude and type of genetic interaction - a negative effect means the guides targeting a gene are selectively depleted in the C9KO (a synthetic lethal interaction) and a positive effect means the guides targeting a gene are selectively enriched in the C9KO population compared to the control population. The confidence score indicates statistical significance. Synthetic lethal genetic interactors that passed the 10% FDR in blue.
