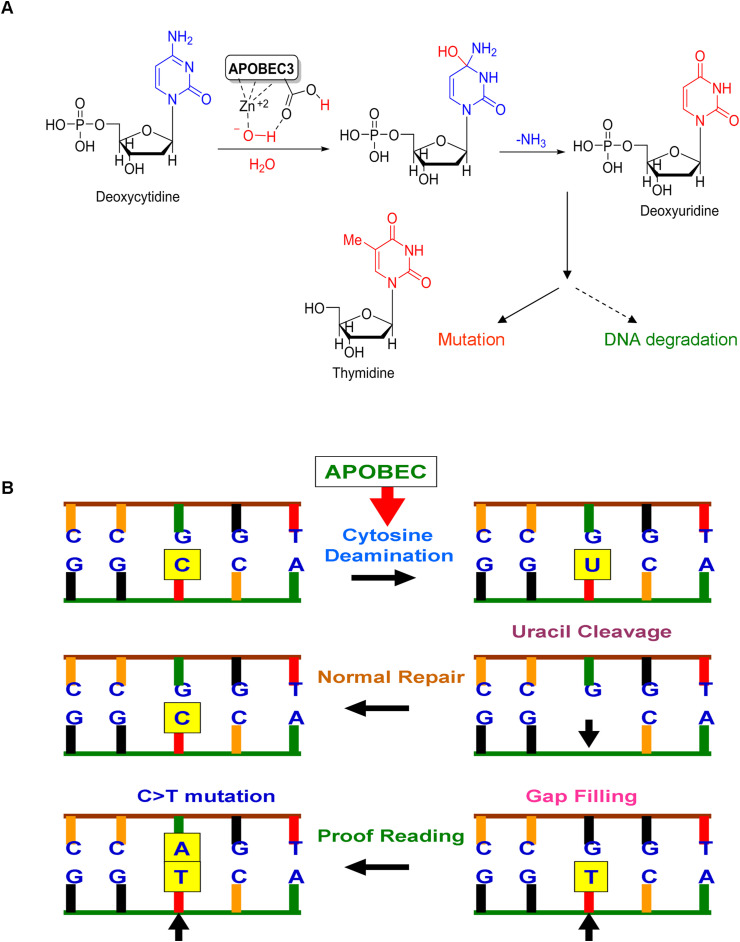
Fig. 2.
Mechanism of APOBEC-mediated cytosine deamination and APOBEC-induced mutations in the host genome.
A) APOBEC-mediated catalytic activity. APOBEC family enzymes catalyze the hydrolytic reaction of cytosine to uracil (C-to-U) and induce DNA degradation or mutations if the APOBEC3-mediated conversion of cytosine to uracil is not repaired. B) Induction of C > T mutation by APOBEC. The illustration shows the C > T mutation resulting from a series of biochemical changes including cytosine deamination and defect in proofreading during replication.