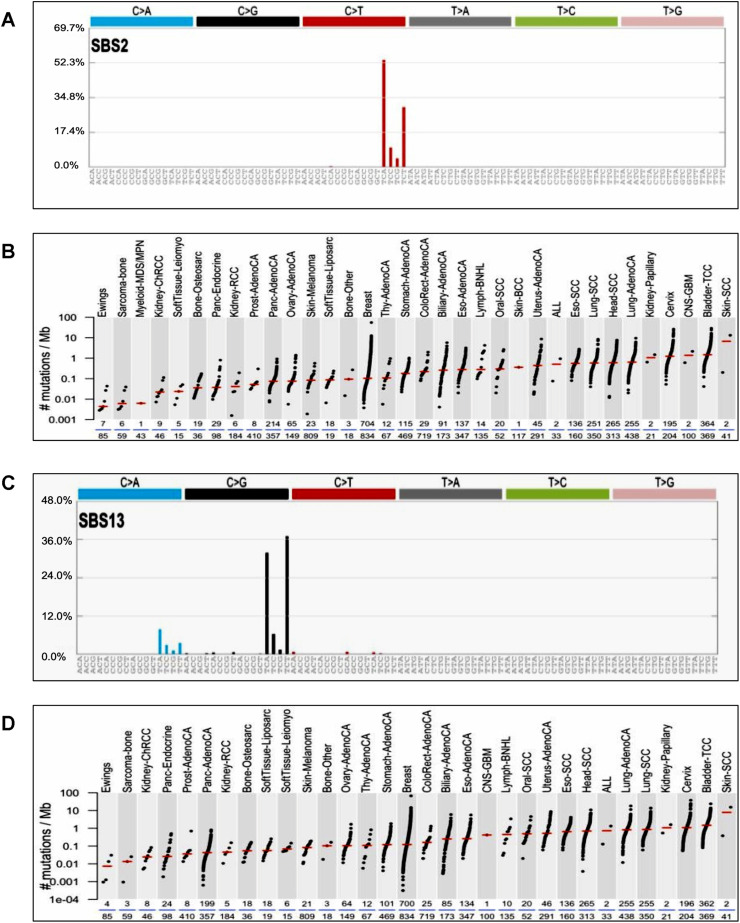
Fig. 3.
APOBEC SBS 2 and 13 signature mutations in cervical cancer.
A) APOBEC SBS2 signature mutations. SBS2 mutations are generated directly by DNA replication across uracil or by error-prone polymerases replicating across abasic sites generated by base excision repair removal of uracil. TCA context mutations are more prevalent >50% than TCC, TCG, and TCT. B) Distribution of APOBEC SBS2 Signature mutations found in human cancers. APOBEC3 SBS2 signature mutations are more frequently observed in cervical and bladder cancers. C) APOBEC SBS13 signature mutations.SBS13 mutations are generated by error-prone polymerases (such as REV1) replicating across abasic sites generated by base excision repair removal of uracil. TCA and TCT context mutations are more common in SBS13 signature mutation. D) Distribution of APOBEC SBS13 signature mutations in human cancers.SBS13 is usually found in the same samples as SBS2. APOBEC3 SBS13 signature mutations are commonly observed in cervical and bladder cancers. (The figure was generated using COSMIC data base).