Figure 6.
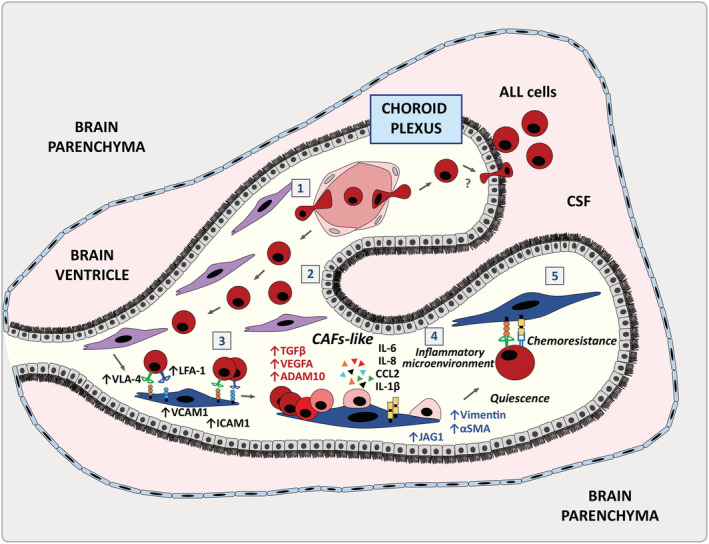
The choroid plexus stroma could act as a sanctuary for B‐cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells. Schematic representation of the involvement of the choroid plexus in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: BCP‐ALL cells could reach the CP via its fenestrated vasculature that can become more permissive under the influence of leukaemic cells (1). Once the CP is colonized, BCP‐ALL cells would preferentially stay in the connective stroma and occasionally move towards the CSF crossing the CP epithelial lining which forms the BCSFB (2). BCP‐ALL cells would then interact with the CP stromal fibroblasts through the upregulated expression of VCAM‐1/VLA‐4 and ICAM‐1/LFA‐1 ligand–receptor pairs (3) and induce a CAF phenotype which would promote a pro‐tumoural inflammatory microenvironment (4). BCP‐ALL cells would remain attached to the CP CAF‐like cells and could acquire quiescence and chemoresistance, a process partially dependent on the VLA‐4 and Notch signalling pathways (5).
