Figure 1.
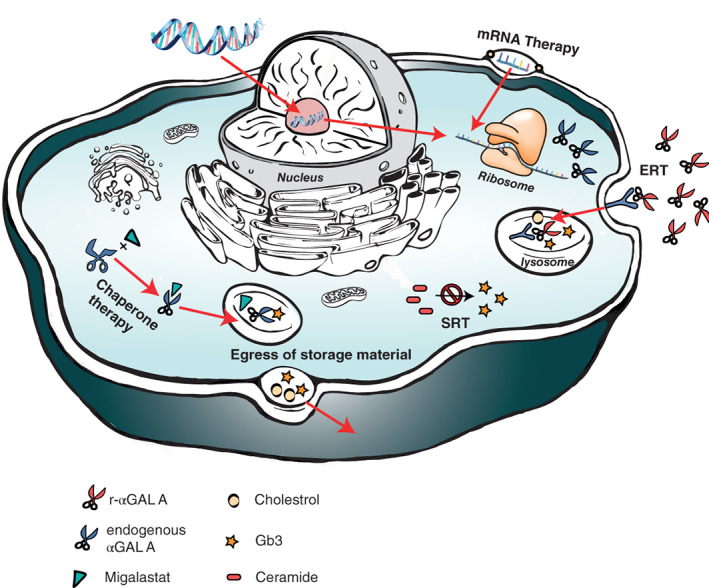
Overview of different approaches in treating Fabry disease; Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) aims to restitute defective αGAL A. Chaperones bind to the active site of the unstable αGAL A to aid proper folding. Substrate reduction therapy targets the glycosphingolipid synthesis to reduce formation of Gb3 and its derivatives. Gene therapy aims to correct the underlying genetic defect of FD. MRNA therapy induces transient endogenous αGAL A production. The egress of Gb3 can potentially be stimulated by enhancing cholesterol efflux (Figure 4). FD, Fabry disease
