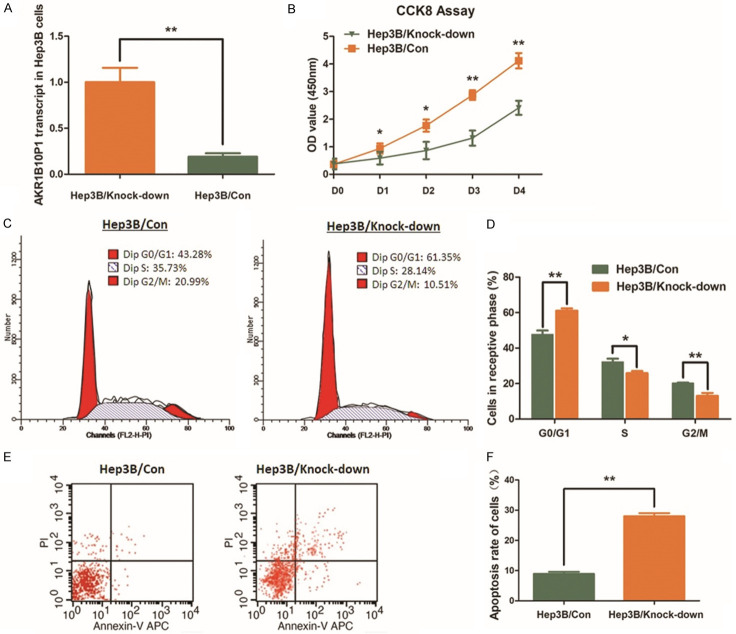
Figure 2.
Knock-down AKR1B10P1 suppresses cell proliferation of Hep3B cells and induces cell apoptosis. A. AKR1B10P1 was knocked-down in Hep3B cells through shRNA transfection. RT-qPCR assay was used for validating the effect of the transfection. A significant defection of AKR1B10P1 expression was observed in the treated cells (**P < 0.01). B. CCK8 assay was applied for investigating the effect of AKR1B10P1 on cell proliferation. The Hep3B cell proliferation was significantly impaired by knocking-down AKR1B10P1. P value was < 0.05 for day 1~2 and was < 0.01 for day 2~4 (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). C. The representative histograms describes the cell cycle profiles of Hep3B cells by using flow cytometry. D. The cell cycle of Hep3B cells was arrested by knocking-down AKR1B10P1. Briefly, after knocking-down AKR1B10P1, the percentage of the cells in G0/G1 phase was increased from 47.66% to 61.13%; the S phase and the G2/M phase were decreased from 28.14% to 25.82% and 20.15% to 13.06% respectively. These results are means of three independent experiments ± SD. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). E. The representative histograms describing cell apoptosis status in Hep3B cells through flow cytometry. F. The apoptosis rate of Hep3B cells was significantly increased from 8.96% to 28.04% (**P < 0.01) via knocking-down AKR1B10P1. The results are means of three independent experiments ± SD. (**P < 0.01).