Figure 8.
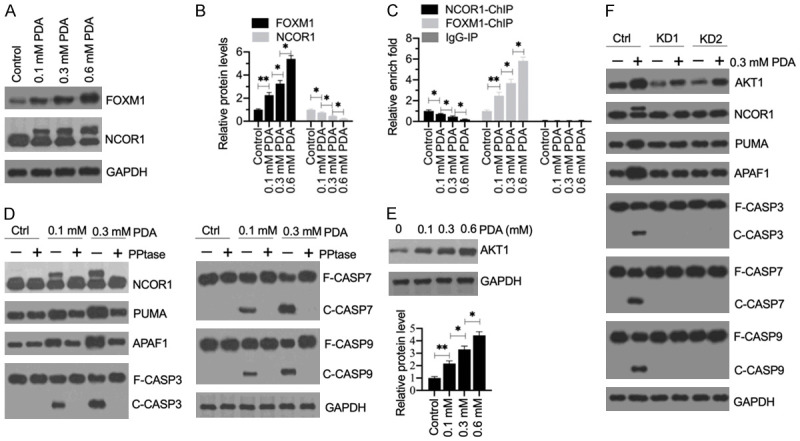
The phosphorylation of NCOR1 mediated by AKT1 was required for the activation of apoptosis signaling. (A) The protein levels of FOXM1 and NCOR1 in PDA-treated cells. Total cell extracts from cells treated with different doses of PDA (0, 0.1, 0.3 and 0.6 mM) were subjected to western blotting to examine the protein levels of FOXM1, NCOR1, and GAPDH (loading control). (B) Quantification of protein band signals. The protein band signals in (A) were quantified using ImageJ software. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01. (C) The occupancy of NCOR1 and FOXM1 on the promoter of PUMA. ChIP assays were performed in the cells used in (A) with anti-NCOR1, anti-FOXM1 and IgG (negative control). The purified input and output DNA samples were subjected to RT-qPCR analysis to examine the occupancy of NCOR1 and FOXM1 on the promoter of PUMA. **P<0.05 and **P<0.01. (D) The effect of phosphatase (PPtase) on NCOR1 and apoptotic proteins. HSMM-1 cells were treated with or without 0.1 and 0.3 mM PDA for 12 h, followed by treating with or without PPtase for 2 h. Total protein extracts were subjected to western blotting to examine the protein levels of NCOR1, PUMA, APAF1, CASP3, CASP7, CASP9, and GAPDH (loading control). (E) The protein levels of AKT1 in PDA-treated cells. The same protein samples as used in (A) were subjected to western blotting to examine the protein levels of AKT1 and GAPDH (loading control). The protein signals were quantified. (F) The effect of AKT1 knockdown on apoptotic proteins. Control-KD (Ctrl), AKT1-KD1 (KD1) and AKT1-KD2 (KD2) cells were treated with or without 0.3 mM PDA for 12 h. Total protein extracts were subjected to western blotting to examine the protein levels of AKT1, NCOR1, PUMA, APAF1, CASP3, CASP7, CASP9, and GAPDH (loading control).
