Figure 9.
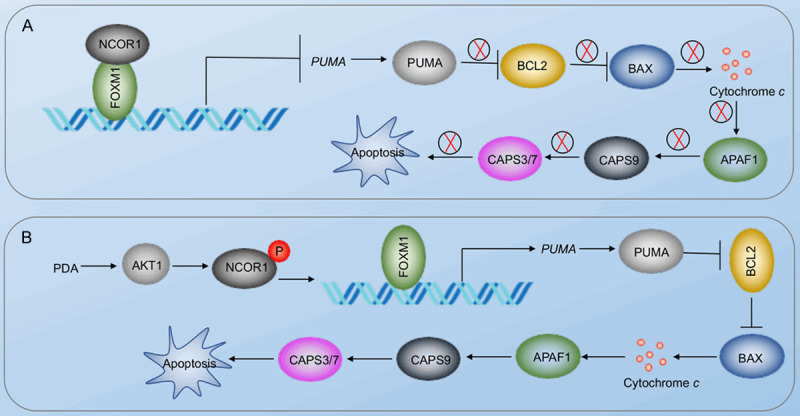
A schematic diagram of PDA-activated apoptosis signaling in the pathogenesis of sarcopenia. A. Schematic diagram of the NCOR1-FOXM1 transcriptional complex in non-sarcopenic muscles. The NCOR1-FOXM1 complex docks on the promoter of PUMA, and NCOR1 functions as a repressor to inhibit the expression of PUMA. The repression of PUMA inhibits its downstream molecules, such as BAX, APAF1, and CASP3/7/9. B. Schematic diagram of PDA-mediated signaling. The accumulation of PDA activates AKT1, causing the phosphorylation of NCOR1. The phosphorylated NCOR1 fails to assemble a complex with FOXM1, leading to the upregulation of PUMA. The induction of PUMA initiates its downstream apoptosis signaling, leading to cell apoptosis and the pathogenesis of sarcopenia.
