Figure 1.
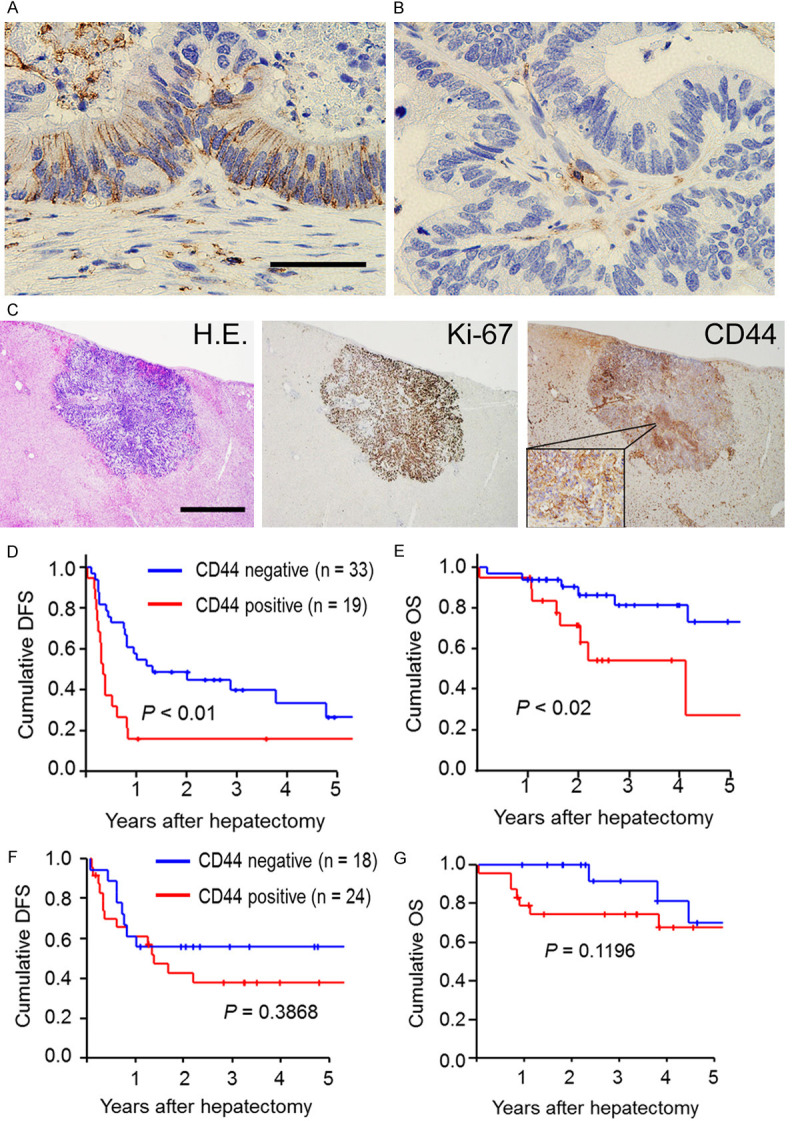
CD44 expression in residual cancer cells after chemotherapy for colorectal liver metastases and its clinical impacts on survival outcomes. (A) A representative picture of membranous CD44-positive expression (Scale bars, 50 µm). (B) A representative picture of membranous CD44-negative expression. (C) Pictures of CD44 and Ki-67 expression in the a residual micrometastasis after chemotherapy. Left) Hematoxylin-eosin staining (Scale bar, 1 mm). Middle) Ki-67 expression. Right) CD44 expression. (D and E) A Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of disease-free survival (D) and overall survival (E) in comparisons between positive and negative CD44 expression in patients who underwent conversion hepatectomy (chemotherapy and then hepatectomy) for initially unresectable colorectal liver metastases. The log-rank test was used. (F and G) A Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of disease-free survival (F) and overall survival (G) in comparisons between positive and negative CD44 expression in patients who underwent straight hepatectomy (without chemotherapy) for initially resectable colorectal liver metastases. The log-rank test was used.
