Figure 1.
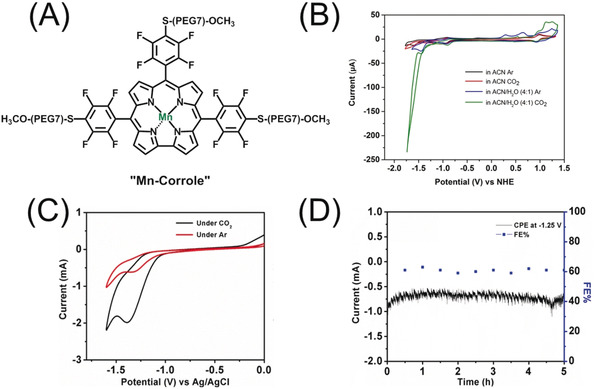
A) Chemical structure of the Mn‐corrole B) cyclic voltammetry of Mn‐corrole dissolved in ACN under Ar (black), CO2 (red), in ACN/H2O (4:1) under Ar (blue) and in ACN/H2O (4:1) under CO2 (green). C) Heterogeneous electrocatalysis of 0.5 mg cm−2 Mn‐corrole on carbon paper electrode under Ar (red) and CO2 (black) at pH 6.0 (Ag/AgCl/1 m KCl, Pt, 100 mV s−1). D) Controlled potential electrolysis of Mn‐corrole immobilized on a carbon paper electrode in 0.1 m phosphate buffer (pH 6) saturated with CO2 at −1.25 V vs. Ag/AgCl for 5 h. All homogeneous cyclic voltammetry measurements were performed with 0.1 m TBAPF6 as supporting electrolyte using glassy carbon as working, platinum wire as counter and a non‐aqueous pseudo‐Ag/AgCl reference electrode at a scan rate of 100 mV s−1.
