Figure 2.
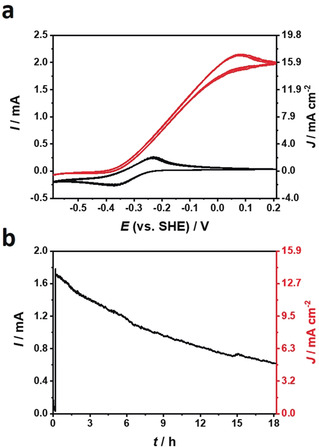
Electrochemical characterization of the redox polymer/DdHydAB‐based bioanode. a) Cyclic voltammograms (5 mV s−1) of a P(GMA‐BA‐PEGMA)‐vio//P(N3MA‐BA‐GMA)‐vio/DdHydAB gas‐diffusion bioanode in the presence of H2 (red traces, three consecutive CVs) and Ar (black traces, three consecutive CVs). B) Chronoamperometry of a P(GMA‐BA‐PEGMA)‐vio//P(N3MA‐BA‐GMA)‐vio/DdHydAB bioanode at an applied potential of +0.16 V vs. SHE and in H2 gas diffusion mode. Working electrolyte: 0.1 m phosphate buffer (pH 7.4); nominal hydrogenase loading: 39.8 nmol cm−2, total polymer loading: 1.8 mg cm−2.
