Figure 2.
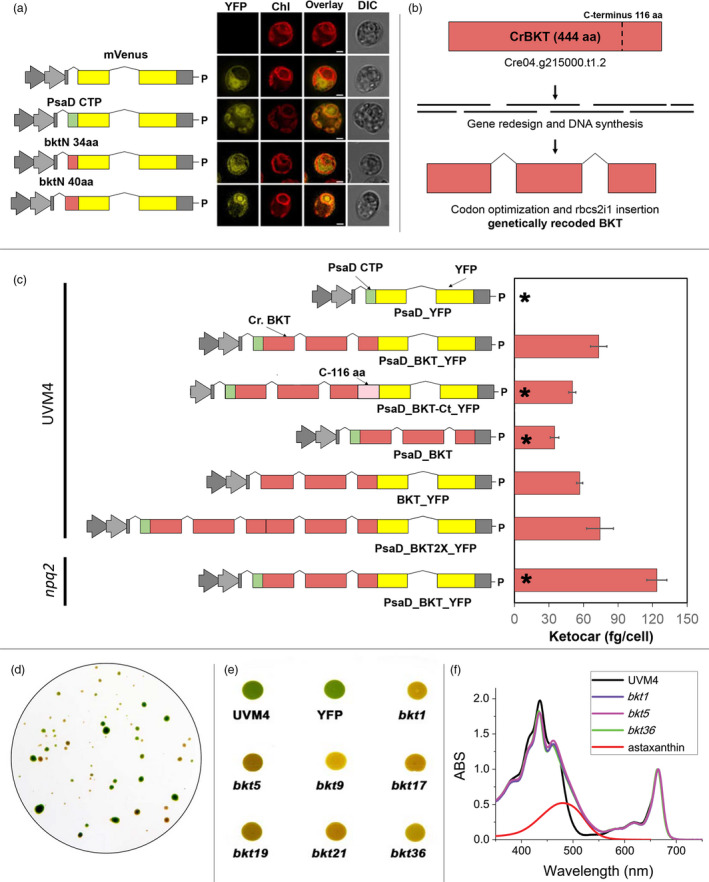
SyntheticCrBKT redesign, expression vectors for Chlamydomonas reinhardtii transformation and phenotypic change in expression lines. (a) Analysis of endogenous CrBKT transit peptide was performed by fusion of two different amino acid lengths of the targeting peptide to the YFP reporter. A cytoplasmic and chloroplast‐targeted control is shown, and the latter is mediated by the previously characterized PsaD chloroplast targeting peptide. YFP fluorescence (YFP), chlorophyll autofluorescence (Chl), merger of these two channels and differential interference contrast (DIC) images are shown. Scale bar represents 2 µm. (b) The optimized CrBKT sequence was built by gene synthesis after in silico design using codon optimization and systematic spreading of the rbcs2 intron 1 sequence to minimize exon lengths as previously described to enable robust transgene expression (Baier et al., 2018b). (c) Schematic overview of all expression vectors used in this work and their respective ketocarotenoid accumulation efficiencies. All gene expression cassettes use the Hsp70A/Rbcs2 hybrid promoter containing rbcs2 intron 1 and its 5′ untranslated region as previously described (Lauersen et al., 2015). PsaD_YFP: YFP localized to the chloroplast by the PsaD transit peptide. PsaD_BKT_YFP: BKT fused to YFP targeted by PsaD transit peptide. PsaD_BKT_cterm_YFP_Paro: same as previous vector with the addition of the 116 C‐terminal amino acid coding extension of the CrBKT gene. BKT_YFP_Paro: BKT fused to YFP targeted by endogenous transit peptide. PsaD_BKT: CrBKT targeted into chloroplast by PsaD transit peptide without the YFP reporter. PsaD_2xBKT_YFP: Two copies of BKT coding sequence were put in frame in order to generate a fused protein carrying two BKT and YFP. For both BKT copies, sequence coding for first 40 aa was removed. All proteins expressed carry a strepII affinity tag (WSHPQFEK*) on the C‐terminus. All the constructs were used to transform UVM4 strain (Neupert et al., 2009b). PsaD_BKT_YFP construct was used to transform the npq2mutant strain, a C. reinhardtii strain mutated on the gene encoding for zeaxanthin epoxidase, resulting into constitutive accumulation of zeaxanthin (Niyogi et al., 1997a). Selection was achieved for all constructs with the AphVIII paromomycin (P) resistance cassette of the pOpt vector backbone. Ketocarotenoid accumulation per cell is expressed as mean ± SD (n = 5). The significantly different value from the one obtained with PsaD BKT_YFP construct is marked with an asterisk (*) (P < 0.05). (d) Orange/red phenotypes of C. reinhardtii cells expressing CrBKT_YFP recovered after transformation and selection on solid medium. (e) Image of UVM4 and transformed cells spotted on TAP agar and grown at 100 µmol/m2/s; YFP represents a strain transformed with PsaD_YFP as a control, and bkt are lines transformed with CrBKT_YFP. (f) Spectra of acetone‐extracted pigments from UVM4 and three select bkt lines. Spectra are normalized to absorption in Qy region. Spectrum of astaxanthin is shown as reference in red.
