Fig. 3.
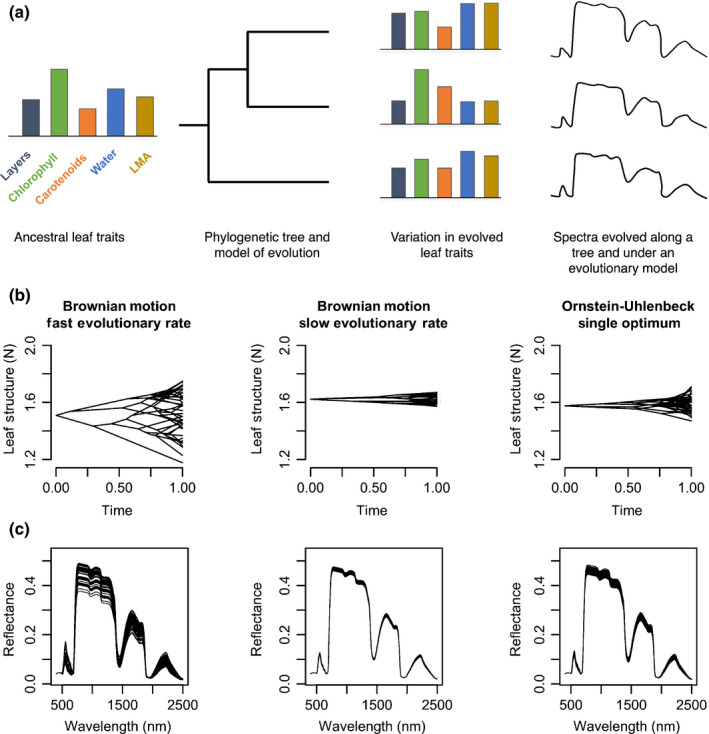
Framework integrating trait evolution and leaf spectral models that enables the estimation of evolutionary parameters from spectra and simulation of leaf spectra along a phylogeny. (a) Ancestral leaf attributes evolve along a phylogenetic tree under a given evolutionary regime, generating the current leaf attributes that underlie spectra. From the evolved leaf attributes, radiative transfer models (RTMs) – such as prospect – estimate spectra that carry the signature of the phylogeny. (b) Evolution of leaf structure according to the unconstrained Brownian motion model, showing that fast rates of evolution result in more trait variation than slow rates. An Ornstein–Uhlenbeck (OU) process models an evolutionary constraint around an optimum trait value and results in less trait variation than an unconstrained Brownian motion model despite having the same rate of evolution. (c) Spectra estimated with the prospect5 model, where all leaf attributes evolved under the same model except for leaf structure, which evolved under the three scenarios outlined earlier.
