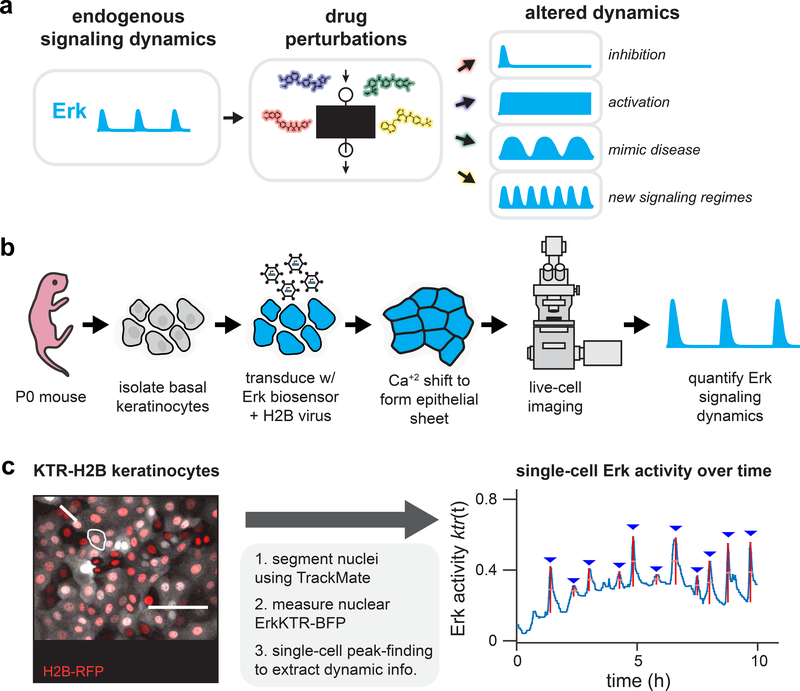
Figure 1. High-throughput screening for altered Erk dynamics.
(A) A small-molecule screen for altered signaling dynamics. Such a screen can identify altered signaling behaviors including total pathway inhibition, constitutive activation, dynamics that resemble disease states, or previously undescribed dynamic regimes. (B) Primary keratinocytes as a model system for quantitative studies of Erk signaling dynamics. Basal epidermal keratinocytes are isolated from a P0 mouse pup, transduced with viral vectors encoding live-cell biosensors, induced to form a uniform epithelial sheet, and imaged via confocal microscopy. (C) An image processing pipeline for monitoring Erk dynamics. A fluorescent nuclear marker enables automated cell segmentation, tracking, and quantification of nuclear Erk kinase translocation reporter (KTR) activity. A representative image of KTR-BFP- and H2B-RFP-expressing primary mouse keratinocytes is shown, as well as quantification of Erk activity from the indicated cell.