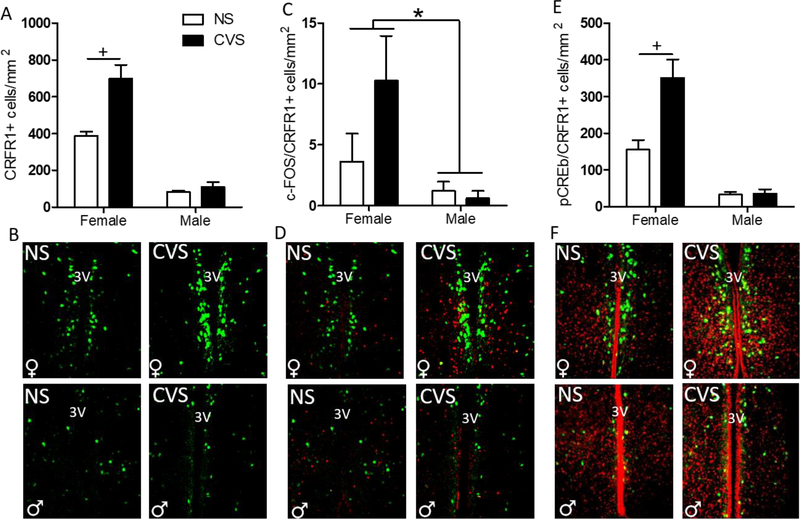
Figure 4. Effects of CVS on the number of AVPV/PeN CRFR1-GFP, c-Fos/CRFR1, and pCREB/CRFR1 cells.
(A) CVS females showed a significant increase in CRFR1-ir compared to all other treatment groups. (B) Representative images of CVS and NS female and male AVPV/PeN CRFR1-GFP. (C) c-Fos/CRFR1-GFP co-expression was significantly higher in all female AVPV/PeN than male, regardless of treatment condition. (D) Representative images of CVS and NS female and male c-Fos/CRFR1-GFP showing a female-specific reduction in c-Fos/CRFR1-GFP cells. (E) Females, regardless of treatment, had increased pCREB/CRFR1-GFP in the AVPV/PeN compared to males, and CVS females specifically had higher pCREB/CRFR1-GFP than any other groups. (F) Representative images of NS and CVS female and male pCREB/CRFR1-GFP in the AVPV/PeN showing female specific increased pCREB. 3V, third ventricle; NS, non-stressed; CVS, chronic variable stress. * Indicates a main effect of sex, (F>M; p < 0.05). + indicates a significant increase in CVS compared to NS females (p < 0.01).