Fig. 5. Oxidative stress is necessary to up-regulate WRAP53 expression and promote its traffic to the nucleus.
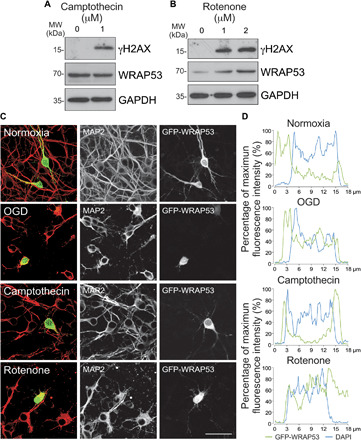
Neurons were treated with the topoisomerase inhibitor, camptothecin, and the mitochondrial inhibitor, rotenone, for 8 and 4 hours, respectively. (A and B) WRAP53 and γH2AX expression levels detected by Western blotting. GAPDH was probed as loading control. Representative blots are shown. Protein abundance quantification from three different neuronal cultures is shown in fig. S5B. (C and D) Neurons were transfected with WRAP53-GFP for 24 hours and were subjected to either OGD, as indicated in Fig. 1, or to camptothecin and rotenone treatments as described above. (C) Representative images of cortical neurons stained with GFP and MAP2 (neuronal marker). Scale bar, 25 μm. (D) Representative cross-sectional intensity profiles for GFP (green) and DAPI (blue) staining of GFP-WRAP53–transfected neurons.
