Fig. 8. The Wrap53 C>G SNP (rs2287499) modulates protein nuclear translocation and functional outcome after stroke.
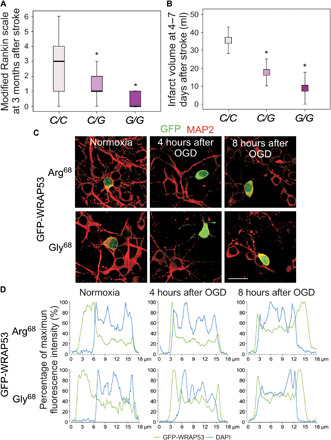
(A and B) The stroke cohort included 408 patients (rs2287499 C/C, 311; C/G, 87; G/G, 10). (A) mRS was used to evaluate the functional outcome of patients at 3 months after stroke. Boxplots show median values (horizontal line inside the box), quartiles (box boundaries), and the largest and smallest observed values (error bars) (*P < 0.0001 versus C/C patients; Mann-Whitney test). (B) Infarct volumes at 4 to 7 days after stroke were measured in patients with indicated Wrap53 genotypes. Data are expressed as means ± SD (*P < 0.0001 versus C/C patients; Student’s t test). (C and D) Neurons were transfected with the two polymorphic variants of WRAP53, Arg68 (ancestral, C allele) and Gly68 (mutant, G allele), fused to GFP (GFP-WRAP53) for 24 hours, and were subjected to OGD, as indicated in Fig. 1. (C) Representative images of cortical neurons stained with GFP and MAP2 (neuronal marker). Scale bar, 25 μm. (D) Representative cross-sectional intensity profiles for GFP (green) and DAPI (blue) staining of GFP-WRAP53 Arg68– and GFP-WRAP53 Gly68–transfected neurons.
